Bank transit numbers play a crucial role in financial transactions, particularly when it comes to transferring funds between banks. If you're unfamiliar with this term, you're not alone. Many people find themselves confused when they first encounter the concept of a bank transit number. In this article, we will delve into the meaning, purpose, and significance of bank transit numbers, providing you with a clear understanding of their function in the banking system.
A bank transit number, often referred to as a routing transit number (RTN) in the United States, is a nine-digit code used to identify a specific financial institution within the banking network. This number ensures that money transfers are directed to the correct bank or credit union. Understanding bank transit numbers is essential for anyone who engages in financial transactions, whether for personal or business purposes.
As the financial world becomes increasingly digital, the importance of bank transit numbers continues to grow. They serve as a vital component in ensuring the accuracy and security of electronic funds transfers, direct deposits, and various other banking activities. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of bank transit numbers and their role in modern banking.
Read also:How To Get Rid Of Gnats In Apartment A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Definition of Bank Transit Number
- Importance of Bank Transit Numbers
- Structure of Bank Transit Numbers
- Types of Bank Transit Numbers
- History and Evolution of Bank Transit Numbers
- Common Uses of Bank Transit Numbers
- How to Find Your Bank Transit Number
- Security Concerns with Bank Transit Numbers
- International Bank Transit Numbers
- The Future of Bank Transit Numbers
Definition of Bank Transit Number
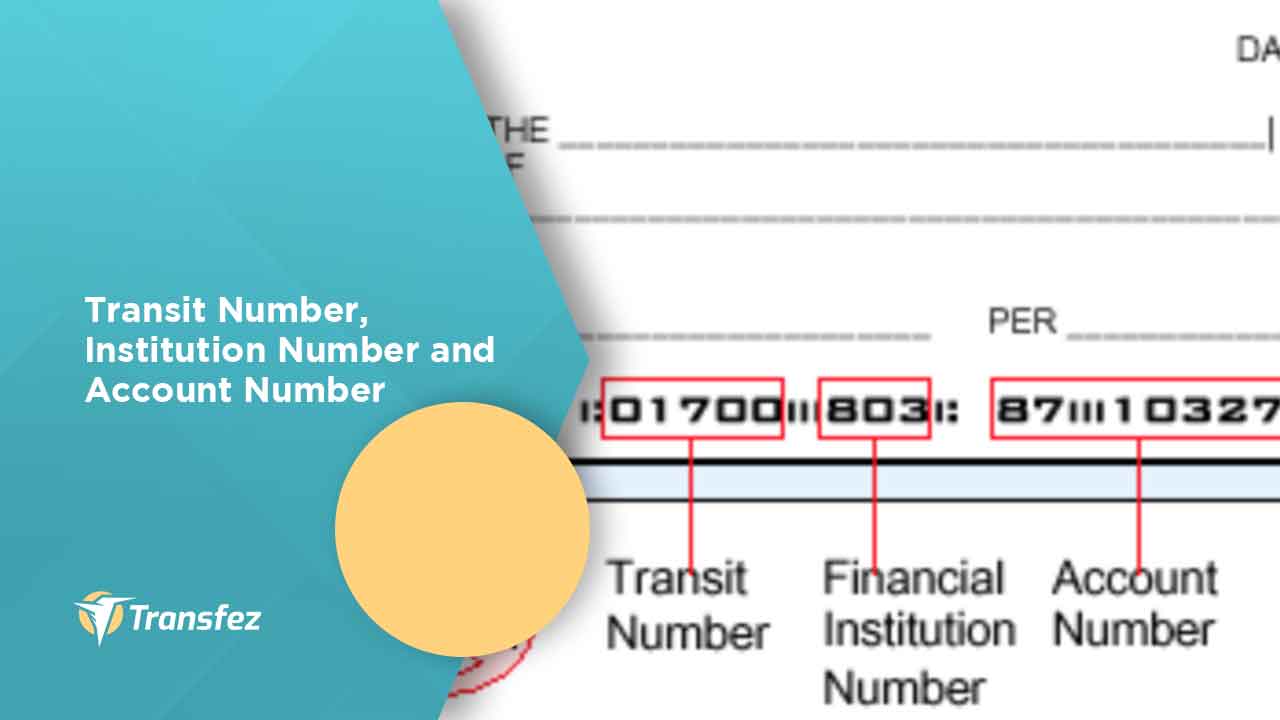
A bank transit number is a unique identifier assigned to a financial institution to facilitate the processing of financial transactions. This number is primarily used in the United States and Canada, where it is known as a routing transit number (RTN) or branch transit number, respectively. The primary purpose of a bank transit number is to ensure that funds are routed to the correct bank or branch during interbank transactions.
Key Components of a Bank Transit Number
Bank transit numbers consist of several components that provide specific information about the financial institution:
- Bank Identifier: The first four digits identify the bank or financial institution.
- Branch Code: The next four digits represent the specific branch of the bank.
- Check Digit: The final digit is a check digit used to verify the accuracy of the number.
Importance of Bank Transit Numbers
Bank transit numbers are critical for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the banking system. They ensure that financial transactions are processed accurately and securely, minimizing the risk of errors or fraud. Without bank transit numbers, it would be challenging to identify the correct bank or branch when transferring funds or processing payments.
Why Bank Transit Numbers Matter
Here are some reasons why bank transit numbers are essential:
- Accuracy: They ensure that funds are directed to the correct bank or branch.
- Security: They help prevent fraud by verifying the legitimacy of financial transactions.
- Efficiency: They streamline the process of transferring funds between banks.
Structure of Bank Transit Numbers
The structure of a bank transit number varies slightly depending on the country and financial institution. In the United States, bank transit numbers are nine digits long, while in Canada, they are composed of five digits followed by a hyphen and three additional digits.
Structure of U.S. Bank Transit Numbers
In the United States, bank transit numbers follow a standardized format:
Read also:Bergin Hartman A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Career And Achievements
- First Four Digits: Identify the Federal Reserve Bank.
- Next Four Digits: Represent the bank's specific routing number.
- Final Digit: Acts as a check digit to validate the number.
Types of Bank Transit Numbers
Bank transit numbers can be categorized based on their function and the type of financial institution they represent. The two main types of bank transit numbers are:
1. ABA Routing Transit Numbers
ABA routing transit numbers are used for processing checks and other paper-based transactions. They are assigned by the American Bankers Association (ABA) and are widely recognized in the United States.
2. ACH Routing Transit Numbers
ACH routing transit numbers are used for electronic transactions, such as direct deposits and automated payments. They are designed to facilitate faster and more efficient processing of financial transactions.
History and Evolution of Bank Transit Numbers
The concept of bank transit numbers dates back to the early 20th century when the need for a standardized system to identify financial institutions became apparent. The American Bankers Association introduced the routing transit number system in 1910 to streamline the processing of checks and other financial instruments.
Modernization of Bank Transit Numbers
Over the years, bank transit numbers have evolved to accommodate the increasing complexity of the financial system. The introduction of electronic banking and digital transactions has necessitated the development of new systems and protocols to ensure the security and efficiency of financial transactions.
Common Uses of Bank Transit Numbers
Bank transit numbers are used in a variety of financial transactions, including:
- Direct Deposits: Ensuring that payroll and other payments are deposited into the correct account.
- Wire Transfers: Facilitating the transfer of funds between banks.
- Bill Payments: Allowing customers to pay bills electronically.
- Check Processing: Verifying the authenticity and routing of checks.
How to Find Your Bank Transit Number
Locating your bank transit number is a straightforward process. Here are some methods to find your bank transit number:
1. Check Your Bank Statement
Your bank transit number is typically listed on your monthly bank statement. It may also appear on your checks or online banking account.
2. Contact Your Bank
If you're unable to locate your bank transit number, you can contact your bank's customer service department for assistance.
Security Concerns with Bank Transit Numbers
While bank transit numbers are essential for facilitating financial transactions, they can also pose security risks if not handled properly. It's important to keep your bank transit number confidential to prevent unauthorized access to your accounts.
Tips for Protecting Your Bank Transit Number
- Shred Sensitive Documents: Dispose of bank statements and checks properly to prevent identity theft.
- Use Secure Connections: Only access your bank account through secure internet connections.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Regularly review your bank statements for suspicious activity.
International Bank Transit Numbers
While bank transit numbers are primarily used in the United States and Canada, similar systems exist in other countries. For example, the International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is used in many European countries to facilitate cross-border transactions.
Key Differences Between IBAN and Bank Transit Numbers
While both systems serve similar purposes, there are key differences between IBAN and bank transit numbers:
- Format: IBANs are longer and include a country code, while bank transit numbers are shorter and country-specific.
- Purpose: IBANs are designed for international transactions, while bank transit numbers are used for domestic transactions.
The Future of Bank Transit Numbers
As technology continues to evolve, the role of bank transit numbers in the financial system is likely to change. The rise of blockchain and cryptocurrency may lead to new systems for identifying financial institutions and processing transactions. However, bank transit numbers will remain a critical component of the banking infrastructure for the foreseeable future.
Emerging Technologies and Bank Transit Numbers
Financial institutions are exploring new technologies to enhance the security and efficiency of bank transit numbers. These innovations include:
- Biometric Authentication: Using biometric data to verify the identity of account holders.
- Artificial Intelligence: Employing AI to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bank transit numbers are an essential component of the modern banking system. They ensure the accuracy, security, and efficiency of financial transactions, making them indispensable for both personal and business banking. By understanding the definition, purpose, and significance of bank transit numbers, you can better navigate the complexities of the financial world.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with bank transit numbers in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into the world of finance and banking.
For further reading, consider consulting the following sources: