Islam and Muslim are two terms that are often used interchangeably, yet they carry distinct meanings and implications. Understanding the difference between the two is crucial in fostering a more informed and respectful dialogue about one of the world's major religions. In this article, we will explore the nuances of Islam vs Muslim, delving into their definitions, historical contexts, and cultural implications.
As the global Muslim population continues to grow, misconceptions about Islam persist, often leading to confusion and misunderstandings. This article aims to clarify these distinctions while promoting a deeper understanding of the religion and its followers. By examining key aspects of Islamic teachings and the diverse practices of Muslims worldwide, we hope to provide clarity and dispel common stereotypes.
This exploration of Islam vs Muslim is not merely academic but also deeply relevant in today's interconnected world. As we navigate issues of identity, faith, and culture, it is essential to approach these topics with an open mind and a commitment to learning. Let’s begin by unpacking the meanings behind these terms and their significance in both religious and societal contexts.
Read also:Dahmer Grandma The Untold Story Of A Life That Shaped The Infamous Serial Killer
Table of Contents
- Understanding Islam: The Core Beliefs and Principles
- Who Are the Muslims? A Global Perspective
- Historical Context: The Origins of Islam
- Key Differences Between Islam and Muslims
- Cultural Diversity Among Muslims
- Common Misconceptions About Islam and Muslims
- The Role of Education in Bridging Gaps
- Challenges Faced by Muslims Today
- Unity in Diversity: Building Bridges
- Conclusion: Moving Forward Together
Understanding Islam: The Core Beliefs and Principles
Islam is one of the world’s major monotheistic religions, practiced by over 1.9 billion people globally. At its core, Islam emphasizes the belief in one God, Allah, and the submission to His will. The word "Islam" itself translates to "peace" and "submission," reflecting the faith's central tenet of surrendering oneself to divine guidance.
Key Pillars of Islam
The Five Pillars of Islam serve as the foundation of the faith, outlining the essential practices that every Muslim is expected to follow. These include:
- Shahada: The declaration of faith in one God and the prophethood of Muhammad.
- Salah: Performing daily prayers.
- Zakat: Giving alms to the poor and needy.
- Sawm: Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan.
- Hajj: Undertaking a pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in a lifetime, if physically and financially able.
These pillars underscore the importance of spiritual devotion, social responsibility, and communal unity in Islam.
Who Are the Muslims? A Global Perspective
While Islam is a universal religion, Muslims are individuals who practice this faith, and they come from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and nationalities. The global Muslim population spans across continents, with significant communities in Asia, Africa, the Middle East, Europe, and the Americas.
Read also:Unlock The Power Of Bods A Comprehensive Guide To Business Object Data Services
Demographics of the Muslim Population
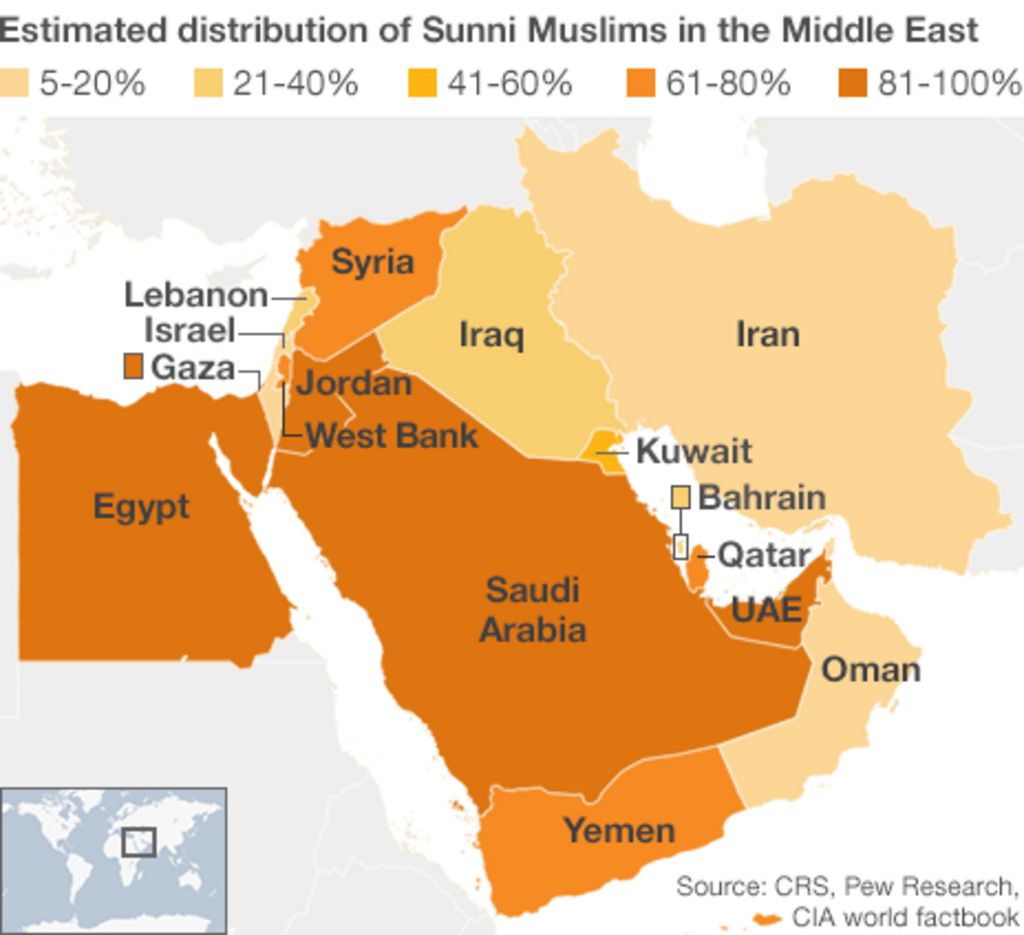
According to the Pew Research Center, Muslims make up approximately 24% of the world’s population. This demographic diversity is reflected in the varied ways Muslims express their faith, influenced by local customs and traditions. Despite these differences, all Muslims share a common belief in the core tenets of Islam.
Historical Context: The Origins of Islam
The history of Islam dates back to the 7th century when the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) received divine revelations in Mecca. These revelations, compiled into the Quran, form the sacred scripture of Islam. The early years of Islam were marked by significant events, including the Hijra (migration) to Medina and the establishment of the first Islamic community.
Key Milestones in Islamic History
Understanding the historical context of Islam is essential in appreciating its evolution and global spread. Some pivotal moments include:
- The revelation of the Quran to Prophet Muhammad.
- The establishment of the first Islamic state in Medina.
- The rapid expansion of the Islamic empire under the caliphates.
- The flourishing of Islamic civilization during the Golden Age.
Key Differences Between Islam and Muslims
While Islam represents the religion and its teachings, Muslims are the people who adhere to these principles. This distinction is crucial in addressing misconceptions and fostering understanding. Islam is a set of beliefs and practices, whereas Muslims are the individuals who interpret and apply these teachings in their daily lives.
How Culture Influences Practice
Cultural practices often shape how Muslims observe their faith, leading to variations in rituals and traditions. For example, Islamic festivals like Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha may be celebrated differently depending on regional customs. These cultural influences highlight the richness and diversity within the Muslim community.
Cultural Diversity Among Muslims
The cultural diversity among Muslims is one of the most fascinating aspects of the faith. From the vibrant colors of Southeast Asian mosques to the intricate calligraphy of Middle Eastern art, the expression of Islam varies widely across the globe. This diversity enriches the global tapestry of Islamic culture and demonstrates the adaptability of the faith.
Examples of Cultural Expression
Some notable examples of cultural diversity in the Muslim world include:
- Traditional clothing such as the hijab, burqa, and thobe.
- Culinary traditions like biryani, kebabs, and baklava.
- Music and poetry inspired by Islamic teachings.
Common Misconceptions About Islam and Muslims
Misconceptions about Islam and Muslims persist due to stereotypes perpetuated by media and cultural misunderstandings. These misconceptions can create barriers to dialogue and cooperation. By addressing these myths, we can promote a more accurate and respectful understanding of the faith and its followers.
Dispelling Stereotypes
Some common misconceptions include:
- Islam promotes violence: This is a gross misrepresentation, as Islam advocates peace and justice.
- All Muslims are the same: Muslims come from diverse backgrounds and practice their faith in various ways.
- Women are oppressed in Islam: Islamic teachings emphasize equality and empower women in many aspects of life.
The Role of Education in Bridging Gaps
Education plays a vital role in dispelling myths and fostering mutual understanding between different cultures and faiths. By promoting interfaith dialogue and cultural exchange, we can build bridges and strengthen community ties. Schools, universities, and community organizations can contribute to this effort by offering programs that highlight the shared values of humanity.
Resources for Learning
For those interested in learning more about Islam and Muslims, several resources are available, including:
- Books and scholarly articles on Islamic history and theology.
- Documentaries and films that explore Muslim culture and traditions.
- Online courses and webinars offered by reputable institutions.
Challenges Faced by Muslims Today
Muslims around the world face numerous challenges, ranging from discrimination and prejudice to political and economic instability. Addressing these issues requires collective efforts from governments, civil society, and individuals to create a more inclusive and equitable world.
Combatting Islamophobia
Islamophobia remains a significant challenge for Muslims globally. Combating this form of bias involves raising awareness, promoting empathy, and fostering dialogue between communities. Initiatives such as interfaith partnerships and community outreach programs can help bridge divides and promote mutual respect.
Unity in Diversity: Building Bridges
Despite the challenges, the Muslim community continues to thrive through unity and resilience. Embracing diversity and celebrating differences can strengthen the bonds within the community and beyond. By working together, Muslims and non-Muslims alike can contribute to a more harmonious and interconnected world.
Steps Toward Unity
Some practical steps toward unity include:
- Engaging in interfaith dialogues and collaborative projects.
- Supporting initiatives that promote cultural exchange and understanding.
- Challenging stereotypes and promoting positive representations of Muslims in media.
Conclusion: Moving Forward Together
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between Islam vs Muslim is essential in fostering a more informed and respectful global community. By exploring the core beliefs of Islam and the diverse practices of Muslims, we can dispel misconceptions and build bridges of understanding. As we move forward, let us commit to promoting education, dialogue, and empathy in our interactions with others.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site that delve into topics related to faith, culture, and global issues. Together, we can create a more inclusive and compassionate world.
Data Source: Pew Research Center