Light dependent reactions are the cornerstone of photosynthesis, a process essential for life on Earth. These reactions occur in the chloroplasts of plant cells and are driven by sunlight. By understanding these reactions, we gain insight into how plants convert light energy into chemical energy, which is crucial for sustaining ecosystems and providing oxygen for life.
Photosynthesis is a complex biological process that converts sunlight into chemical energy. At the heart of this process lies the light dependent reactions, which harness solar energy to produce ATP and NADPH—energy carriers used in the subsequent stages of photosynthesis. This article will explore the intricate mechanisms of these reactions, their importance, and how they impact our environment.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the science behind light dependent reactions, including their role in the overall photosynthesis process, the structures involved, and the chemical reactions that take place. By the end of this article, you'll have a deeper understanding of how plants generate energy and contribute to the global ecosystem.
Read also:How Tall Is Russell Crowe In Feet Discover The Height And More About This Renowned Actor
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Light Dependent Reactions
- Structure of Chloroplasts
- How Light Dependent Reactions Work
- The Role of Photosystems
- Electron Transport Chain
- Energy Conversion in Light Dependent Reactions
- Enzymes and Proteins Involved
- Importance of Light Dependent Reactions
- Applications in Science and Technology
- Future Research Directions
Introduction to Light Dependent Reactions
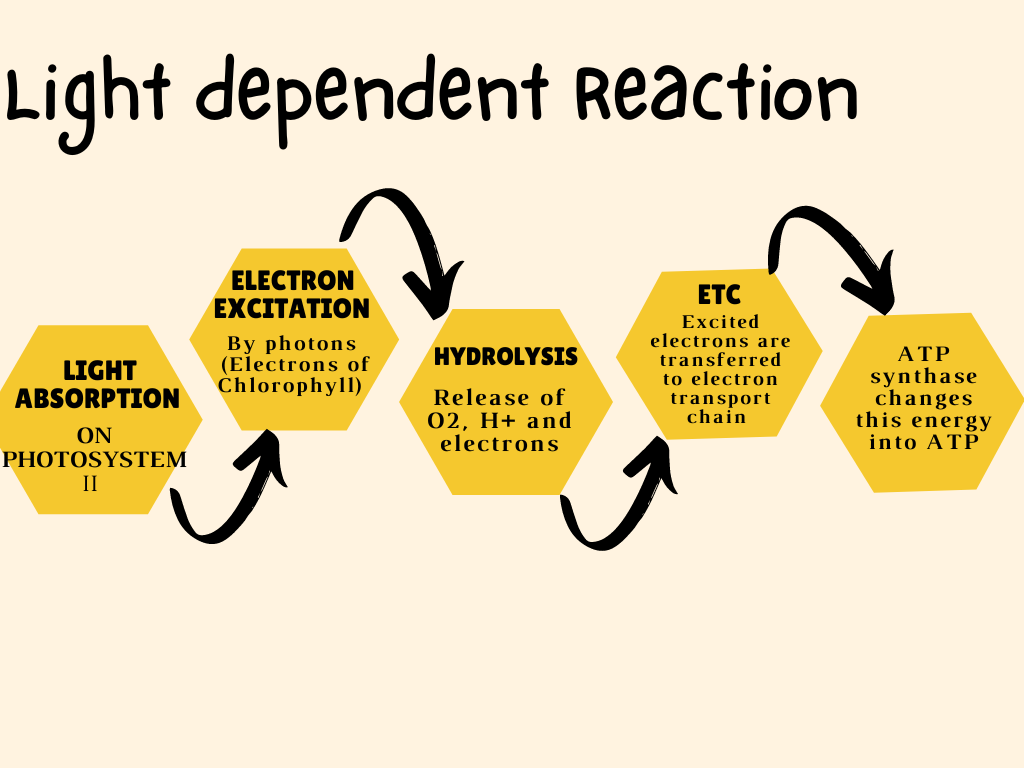
Light dependent reactions are the first stage of photosynthesis, where sunlight is captured and converted into chemical energy. These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involve the splitting of water molecules to release oxygen, electrons, and protons. The energy captured from sunlight is used to produce ATP and NADPH, which are vital for the Calvin cycle, the second stage of photosynthesis.
The process begins when photons of light strike pigments in the photosystems, exciting electrons to higher energy states. This excitation triggers a series of events that lead to the production of energy-rich molecules. Understanding these reactions is crucial for comprehending how plants produce food and oxygen, which are essential for life on Earth.
Why Are Light Dependent Reactions Important?
Without light dependent reactions, photosynthesis would not be possible. These reactions provide the energy necessary for plants to synthesize glucose, a molecule that serves as a primary energy source for both plants and animals. Additionally, the oxygen released during these reactions supports aerobic life forms, making them vital for the survival of most living organisms.
Structure of Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in plant cells that facilitate photosynthesis. They contain thylakoid membranes, where light dependent reactions take place. These membranes are stacked into structures called grana, which are interconnected by stroma lamellae. The stroma, a fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoids, is where the Calvin cycle occurs.
Key Components of Chloroplasts
- Thylakoid membranes: Site of light dependent reactions.
- Grana: Stacked thylakoids that increase surface area for light absorption.
- Stroma: Location of the Calvin cycle and site of ATP and NADPH utilization.
How Light Dependent Reactions Work
Light dependent reactions begin with the absorption of light by pigments such as chlorophyll. This energy excites electrons, which are then transferred through a series of proteins and molecules in the electron transport chain. As electrons move through the chain, they drive the production of ATP and NADPH, essential molecules for the Calvin cycle.
Steps in Light Dependent Reactions
- Light absorption by chlorophyll and other pigments.
- Excitation of electrons and their transfer through the electron transport chain.
- Production of ATP via chemiosmosis.
- Conversion of NADP+ to NADPH.
The Role of Photosystems
Photosystems are protein complexes embedded in the thylakoid membranes that capture light energy. There are two main types: Photosystem II (PSII) and Photosystem I (PSI). PSII is responsible for splitting water molecules and releasing oxygen, while PSI focuses on generating NADPH through the transfer of high-energy electrons.
Read also:Mackenyu Maeda Wife Unveiling The Life And Journey Of A Rising Stars Partner
How Photosystems Function
Each photosystem contains a reaction center surrounded by light-harvesting complexes. When photons strike these complexes, electrons are excited and transferred to the electron transport chain. This process ensures a continuous flow of energy and electrons, enabling the production of ATP and NADPH.
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain is a series of proteins and molecules that transfer electrons from one carrier to another. This movement of electrons creates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane, which is used to drive ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis. The chain also facilitates the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH, a crucial step in photosynthesis.
Components of the Electron Transport Chain
- Cytochrome b6f complex: Facilitates proton pumping and electron transfer.
- Plastoquinone: Transfers electrons between PSII and cytochrome b6f.
- Plastocyanin: Transfers electrons to PSI.
Energy Conversion in Light Dependent Reactions
Light dependent reactions involve the conversion of light energy into chemical energy. This process occurs through the excitation of electrons and their transfer through the electron transport chain. The energy derived from these reactions is stored in the form of ATP and NADPH, which are used in the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
Efficiency of Energy Conversion
Photosynthesis is a highly efficient process, with light dependent reactions converting approximately 3-6% of absorbed solar energy into chemical energy. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining the energy balance in ecosystems and supporting life on Earth.
Enzymes and Proteins Involved
Several enzymes and proteins play critical roles in light dependent reactions. For example, ATP synthase facilitates the production of ATP through chemiosmosis, while ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (FNR) reduces NADP+ to NADPH. These enzymes ensure the smooth operation of the electron transport chain and the efficient conversion of energy.
Key Enzymes in Light Dependent Reactions
- ATP synthase: Produces ATP by utilizing the proton gradient.
- Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase: Converts NADP+ to NADPH.
Importance of Light Dependent Reactions
Light dependent reactions are vital for the survival of plants and, by extension, all life on Earth. They provide the energy necessary for photosynthesis, which produces oxygen and glucose. This process supports ecosystems, regulates atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, and contributes to global food security.
Environmental Impact
The oxygen released during light dependent reactions is essential for aerobic organisms, while the glucose produced supports food chains and provides energy for human consumption. By understanding these reactions, scientists can develop strategies to enhance crop yields and combat climate change.
Applications in Science and Technology
The study of light dependent reactions has led to numerous applications in science and technology. For example, researchers are exploring artificial photosynthesis as a means of producing renewable energy. Additionally, understanding these reactions can inform agricultural practices, leading to more sustainable and efficient farming methods.
Potential Uses of Artificial Photosynthesis
- Production of clean fuels such as hydrogen.
- Development of bio-inspired solar panels.
Future Research Directions
Ongoing research aims to unravel the complexities of light dependent reactions and their potential applications. Scientists are investigating ways to enhance photosynthetic efficiency, develop new materials for artificial photosynthesis, and explore the role of these reactions in combating climate change.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in fully understanding and optimizing light dependent reactions. However, advancements in technology and interdisciplinary research offer promising opportunities for breakthroughs in this field.
Conclusion
Light dependent reactions are a fundamental aspect of photosynthesis, enabling plants to convert sunlight into chemical energy. By understanding these reactions, we gain insight into the processes that sustain life on Earth and pave the way for innovative solutions in science and technology. We encourage readers to explore further and share their thoughts in the comments below. Additionally, consider reading our other articles on related topics to deepen your knowledge of photosynthesis and its importance.