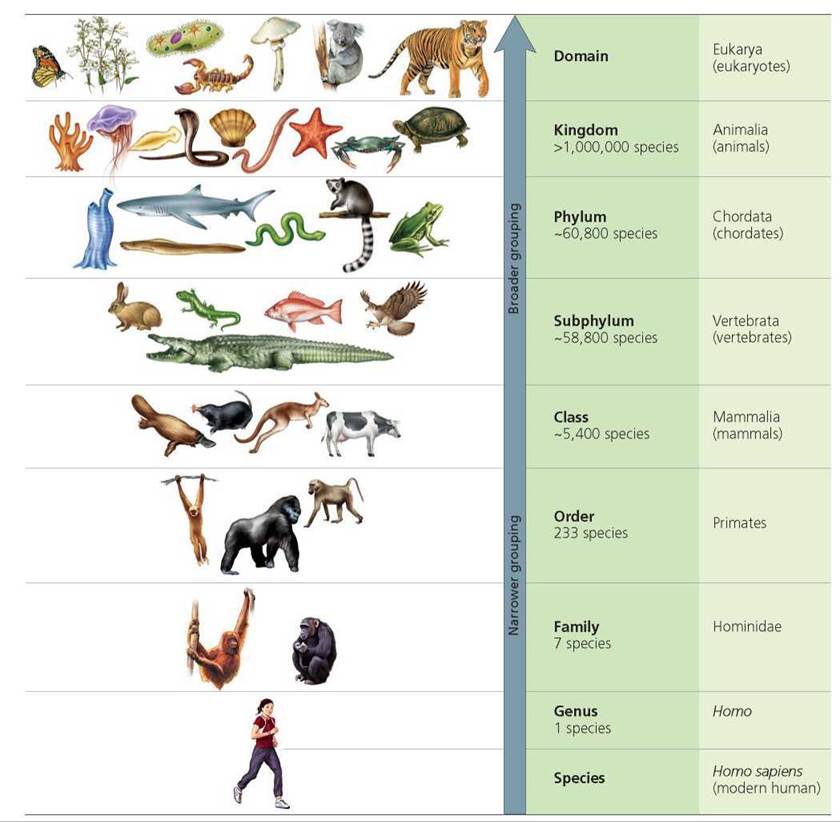
Biological classification is a fundamental aspect of understanding the living world around us, and the hierarchy of Kingdom Phylum Class forms the backbone of this system. This classification system helps scientists categorize organisms systematically, making it easier to study and understand their relationships. By delving deeper into the concept of Kingdom Phylum Class, we can gain a better understanding of how life on Earth is organized.
From the smallest microorganisms to the largest mammals, every living organism can be classified into a specific group based on shared characteristics. This hierarchical system is not only crucial for biologists but also plays an essential role in conservation efforts, medical research, and ecological studies. Understanding this classification framework allows us to appreciate the diversity of life on our planet.
This article will explore the intricate details of Kingdom Phylum Class, including its historical development, practical applications, and its importance in modern biology. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the natural world, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential biological concept.
Read also:Kiko Klout The Rising Star In The World Of Entertainment
Table of Contents
- What is Biological Classification?
- Understanding Kingdom
- Exploring Phylum
- The Role of Class
- The History of Biological Classification
- Taxonomic Ranks Beyond Kingdom Phylum Class
- Methods of Classification
- The Importance of Kingdom Phylum Class
- Examples of Kingdom Phylum Class
- The Future of Biological Classification
What is Biological Classification?
Biological classification is the process of categorizing living organisms into groups based on shared characteristics. This systematic organization allows scientists to identify, name, and study organisms efficiently. The classification system is hierarchical, meaning it consists of several levels, with Kingdom, Phylum, and Class being among the most important.
Carl Linnaeus, often referred to as the "Father of Taxonomy," introduced the binomial nomenclature system, which laid the foundation for modern biological classification. This system uses two names—genus and species—to uniquely identify each organism. However, the broader classification framework, including Kingdom Phylum Class, provides a more comprehensive view of the relationships between different organisms.
Understanding Kingdom
Definition and Importance
The Kingdom is the highest rank in the biological classification system, representing the broadest grouping of organisms. It is based on fundamental characteristics such as cell structure, mode of nutrition, and reproduction. Traditionally, there were five kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. However, advancements in molecular biology have led to the development of the three-domain system: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
- Bacteria: Single-celled organisms without a nucleus.
- Archaea: Similar to bacteria but genetically and biochemically distinct.
- Eukarya: Organisms with complex cells containing a nucleus and organelles.
Exploring Phylum
Subdivision Within Kingdom
Phylum is the second major rank in the classification system, dividing organisms within a kingdom into more specific groups. For example, in the Animal Kingdom, there are over 30 phyla, each representing a distinct body plan. Some of the major phyla include Chordata (vertebrates), Arthropoda (insects and crustaceans), and Mollusca (snails and clams).
Phyla are defined by shared anatomical and physiological traits. For instance, all members of the phylum Chordata possess a notochord, a dorsal nerve cord, and gill slits at some point in their development. These characteristics help scientists identify and classify organisms accurately.
The Role of Class
Further Refinement of Classification
Class is a rank below Phylum and above Order in the biological classification hierarchy. It provides a more detailed categorization of organisms, grouping them based on specific traits. For example, within the phylum Chordata, the class Mammalia includes all mammals, characterized by features such as hair, mammary glands, and live birth (in most cases).
Read also:Jamie Belushi A Comprehensive Look At The Legendary Comedian And Actor
Classes are essential for narrowing down the classification process, allowing scientists to focus on specific groups of organisms with shared characteristics. This level of detail is particularly useful in fields such as ecology, where understanding the relationships between different species is crucial.
The History of Biological Classification
From Aristotle to Modern Taxonomy
The concept of biological classification dates back to ancient times, with Aristotle being one of the first to attempt a systematic organization of living organisms. However, it was Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century who revolutionized the field with his binomial nomenclature system. Linnaeus's work laid the foundation for modern taxonomy, which has since evolved to incorporate advancements in genetics and molecular biology.
Today, the classification system continues to evolve, with new discoveries and technologies providing insights into the relationships between organisms. The development of DNA sequencing, for example, has allowed scientists to classify organisms based on genetic similarities, leading to a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of life on Earth.
Taxonomic Ranks Beyond Kingdom Phylum Class
Order, Family, Genus, and Species
While Kingdom, Phylum, and Class are essential components of the classification system, there are additional ranks that provide even more detail. These include Order, Family, Genus, and Species, each representing a more specific grouping of organisms.
- Order: A rank below Class and above Family, grouping organisms with shared characteristics.
- Family: A rank below Order and above Genus, further refining the classification process.
- Genus: A rank below Family and above Species, typically consisting of closely related species.
- Species: The most specific rank, representing a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
Methods of Classification
Traditional vs. Modern Approaches
Classification methods have evolved significantly over time. Traditional approaches relied heavily on morphological characteristics, such as physical appearance and structure. While these methods are still valuable, modern techniques incorporate molecular data, such as DNA sequences, to provide a more accurate classification.
The integration of molecular data has led to the discovery of new relationships between organisms, challenging long-held assumptions about the classification system. For example, the reclassification of certain species based on genetic evidence has reshaped our understanding of evolutionary relationships.
The Importance of Kingdom Phylum Class
Applications in Science and Society
The classification system, particularly the hierarchy of Kingdom Phylum Class, plays a vital role in various scientific disciplines. In ecology, it helps researchers understand the interactions between different species and their environments. In medicine, it aids in the identification and treatment of diseases caused by microorganisms. In conservation, it provides a framework for protecting endangered species and preserving biodiversity.
Beyond scientific applications, the classification system also has cultural and educational significance. It fosters a deeper appreciation for the diversity of life and encourages curiosity about the natural world. By understanding the relationships between different organisms, we can better appreciate our place in the ecosystem.
Examples of Kingdom Phylum Class
Case Studies in Classification
Let's explore some examples of how Kingdom Phylum Class is applied in practice:
- Homo sapiens: Kingdom: Animalia, Phylum: Chordata, Class: Mammalia.
- Acer saccharum: Kingdom: Plantae, Phylum: Tracheophyta, Class: Magnoliopsida.
- Escherichia coli: Kingdom: Bacteria, Phylum: Proteobacteria, Class: Gammaproteobacteria.
These examples illustrate how the classification system provides a standardized framework for identifying and categorizing organisms, regardless of their complexity or size.
The Future of Biological Classification
Emerging Trends and Technologies
As technology continues to advance, the field of biological classification is poised for significant developments. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in analyzing genetic data promises to enhance our ability to classify organisms accurately and efficiently. Additionally, the discovery of new species and the study of extremophiles (organisms living in extreme environments) will continue to expand our understanding of life on Earth.
Looking ahead, the classification system will likely become even more dynamic, incorporating new data and methodologies to reflect the ever-evolving nature of life. This adaptability ensures that the system remains relevant and useful for future generations of scientists and researchers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the hierarchy of Kingdom Phylum Class is a cornerstone of biological classification, providing a systematic framework for understanding the diversity of life on Earth. From its historical roots to its modern applications, this classification system continues to play a vital role in scientific research and education. By exploring the intricacies of Kingdom Phylum Class, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and interconnectedness of the natural world.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the fascinating realm of biology. Together, let's continue to expand our knowledge and appreciation of the living world.
Data Sources:
- Encyclopedia Britannica
- National Geographic
- NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information)