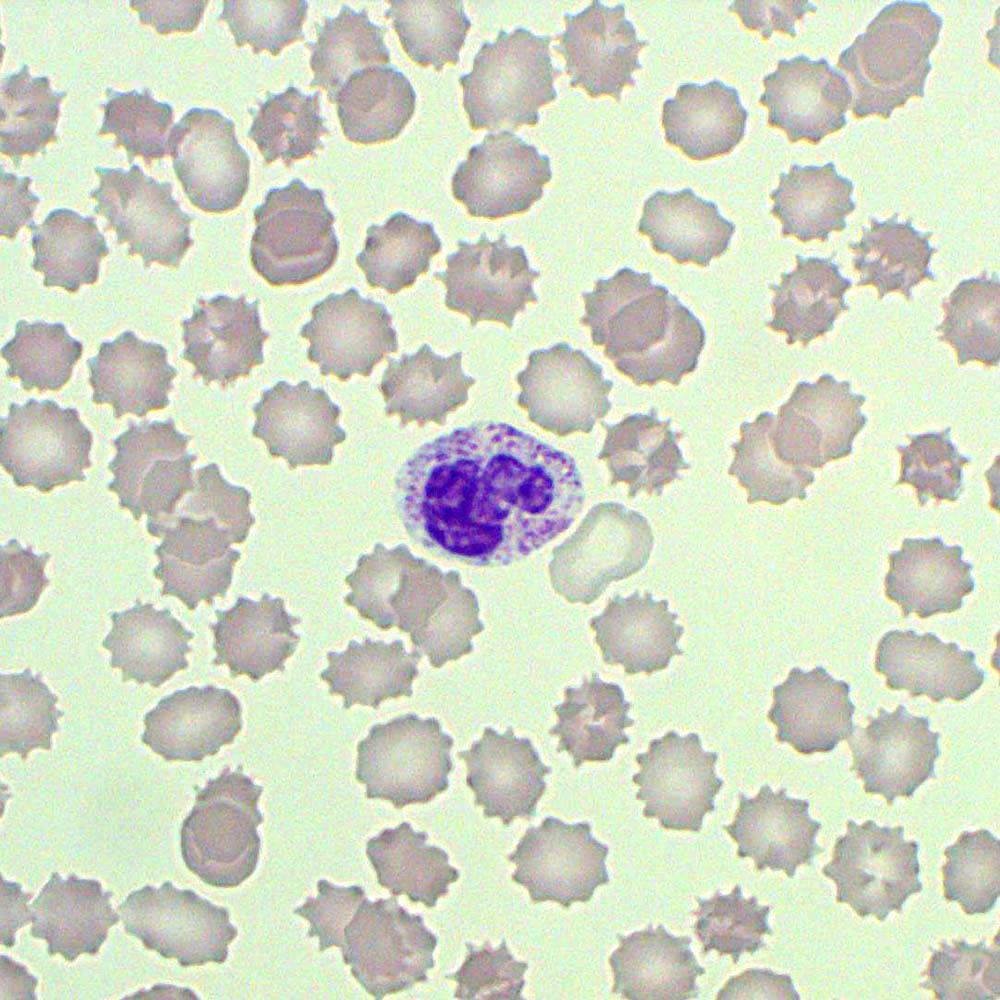
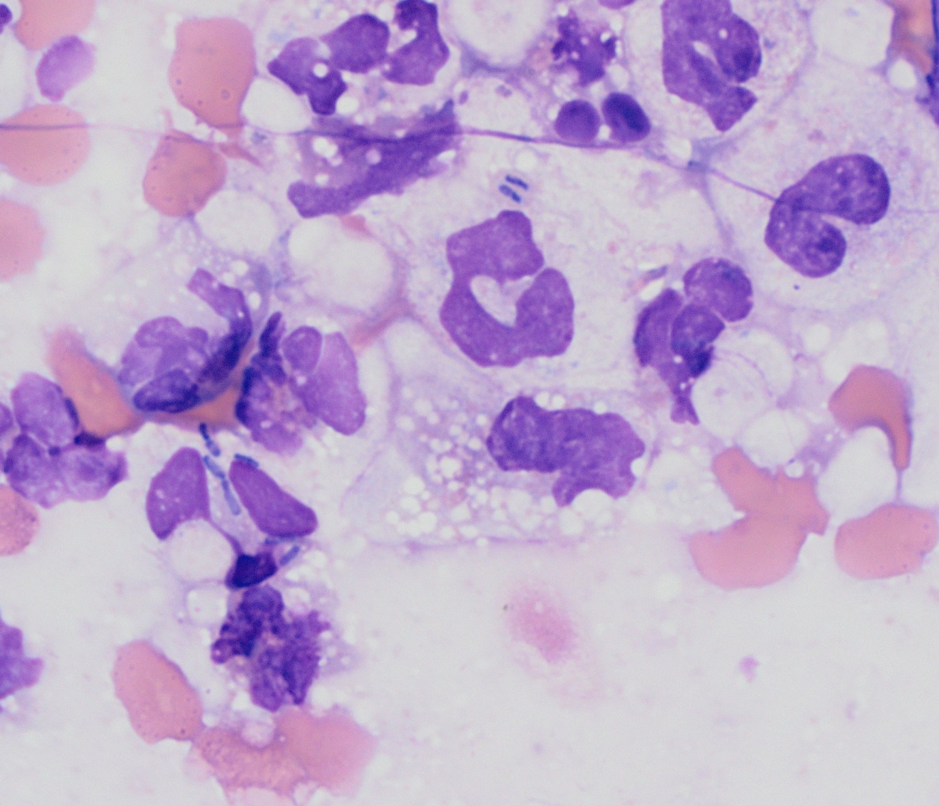
Discovering the world of veterinary science, toxic neutrophils in dogs is an alarming condition that every pet owner should understand. Recognizing the signs and seeking early intervention can significantly improve your dog's health and quality of life. Toxic neutrophils are a critical indicator of severe infections or systemic illness, making awareness and vigilance crucial for responsible pet care.
Toxic neutrophils in dogs represent an essential diagnostic tool for veterinarians. These abnormal cells appear in blood tests when a dog is battling a severe infection or inflammation. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms can help pet owners detect potential health issues early and take necessary action.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about toxic neutrophils in dogs, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Whether you're a seasoned pet owner or a new dog parent, this information can help you ensure the well-being of your furry companion.
Read also:Who Is Kiki Klout The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Her Influence
Table of Contents
- What Are Toxic Neutrophils?
- Causes of Toxic Neutrophils in Dogs
- Symptoms of Toxic Neutrophils
- Diagnosing Toxic Neutrophils
- Treatment Options
- Preventing Toxic Neutrophils
- The Impact on Dog Health
- Factors Contributing to Toxic Neutrophils
- Long-Term Management
- Conclusion
What Are Toxic Neutrophils?
Toxic neutrophils in dogs refer to abnormal changes in neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that plays a critical role in fighting infections. These changes indicate that the body is under severe stress, often due to bacterial infections, inflammation, or other systemic illnesses. Veterinarians detect toxic neutrophils through blood tests, which are essential for diagnosing serious conditions.
Neutrophils are the first line of defense against infections, and their presence in the bloodstream is vital for maintaining a dog's health. However, when these cells become toxic, it signals that the dog's immune system is overwhelmed, and immediate medical attention is necessary.
How Are Toxic Neutrophils Identified?
Veterinarians identify toxic neutrophils through a complete blood count (CBC) test. During this test, the appearance and structure of neutrophils are examined under a microscope. Toxic changes include features such as Dohle bodies, cytoplasmic vacuoles, and toxic granulation, all of which indicate that the neutrophils are immature or stressed.
Early detection of toxic neutrophils can help veterinarians pinpoint the underlying cause and initiate appropriate treatment, improving the dog's prognosis.
Causes of Toxic Neutrophils in Dogs
Several factors can lead to the development of toxic neutrophils in dogs. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and prevention of the condition. Below are some of the primary causes:
- Bacterial infections, such as sepsis or pyometra
- Severe systemic inflammation, including pancreatitis or immune-mediated diseases
- Viral infections, such as parvovirus or distemper
- Toxins or poison exposure
- Stress or trauma
Each of these causes affects the body differently, but they all result in the production of toxic neutrophils. Recognizing the specific cause is essential for tailoring the treatment plan to the dog's needs.
Read also:Delilah Dagger Ethnicity Unveiling Her Cultural Roots
Common Conditions Leading to Toxic Neutrophils
Some conditions are more commonly associated with toxic neutrophils than others. For example, sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection, is a frequent cause. Similarly, pyometra, an infection of the uterus, is often seen in unspayed female dogs and can lead to the development of toxic neutrophils.
Symptoms of Toxic Neutrophils
The symptoms of toxic neutrophils in dogs can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, there are some common signs that pet owners should watch for:
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Lethargy
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Difficulty breathing
These symptoms often indicate that the dog is fighting a severe infection or dealing with systemic inflammation. If your dog exhibits any of these signs, it's important to seek veterinary care promptly.
Recognizing the Early Signs
Early recognition of symptoms is critical for preventing complications. Owners who are familiar with their dog's normal behavior and health patterns are better equipped to notice changes that may indicate the presence of toxic neutrophils.
Diagnosing Toxic Neutrophils
Diagnosing toxic neutrophils involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Veterinarians typically begin with a thorough physical examination to assess the dog's overall health. This is followed by a complete blood count (CBC) to identify abnormal neutrophils.
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of the toxic neutrophils. These may include:
- Culture and sensitivity tests to identify specific bacteria
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays or ultrasound
- Specialized blood tests for viral infections
These diagnostic tools help veterinarians develop a comprehensive understanding of the dog's condition and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
The treatment for toxic neutrophils in dogs depends on the underlying cause. In many cases, antibiotics are prescribed to combat bacterial infections. For viral infections, supportive care may be necessary to manage symptoms while the immune system fights the virus.
In addition to medication, other treatment options may include:
- Fluid therapy to address dehydration
- Pain management
- Nutritional support
Close monitoring and follow-up care are essential to ensure the dog's recovery and prevent recurrence.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is critical for improving the prognosis of dogs with toxic neutrophils. Delayed treatment can lead to complications and worsen the dog's condition. Pet owners should prioritize regular veterinary check-ups and seek care at the first sign of illness.
Preventing Toxic Neutrophils
Preventing toxic neutrophils involves maintaining your dog's overall health and minimizing exposure to potential triggers. Some preventive measures include:
- Regular vaccinations to protect against viral infections
- Spaying or neutering to reduce the risk of reproductive infections
- Proper parasite control
- A balanced diet and regular exercise
By taking these steps, pet owners can help reduce the likelihood of their dogs developing toxic neutrophils and associated health issues.
Regular Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary care is one of the most effective ways to prevent toxic neutrophils. Routine check-ups allow veterinarians to monitor your dog's health and address potential issues before they become serious.
The Impact on Dog Health
Toxic neutrophils can have a significant impact on a dog's health and well-being. The presence of these abnormal cells indicates that the dog's immune system is under severe stress, which can lead to long-term health issues if left untreated. Chronic conditions, such as immune-mediated diseases, can also contribute to the development of toxic neutrophils, further complicating the dog's health.
Managing Chronic Conditions
For dogs with chronic conditions, managing the disease is crucial for preventing the recurrence of toxic neutrophils. This may involve ongoing medication, dietary changes, and regular monitoring by a veterinarian.
Factors Contributing to Toxic Neutrophils
Several factors can contribute to the development of toxic neutrophils in dogs. Age, breed, and overall health status can all play a role. For example, older dogs or those with weakened immune systems may be more susceptible to infections that lead to toxic neutrophils.
Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or stress, can also increase the risk. Understanding these factors can help pet owners take proactive steps to protect their dogs' health.
Breed-Specific Considerations
Certain breeds may be more prone to specific health conditions that can lead to toxic neutrophils. For example, brachycephalic breeds, such as Bulldogs and Pugs, may be more susceptible to respiratory infections, which can contribute to the development of toxic neutrophils.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management of toxic neutrophils involves a combination of preventive care, regular monitoring, and prompt treatment of any underlying conditions. Pet owners should work closely with their veterinarians to develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses their dog's unique needs.
Education and awareness are also key components of long-term management. By staying informed about the latest developments in veterinary medicine, pet owners can ensure that their dogs receive the best possible care.
Building a Strong Relationship with Your Veterinarian
Building a strong relationship with your veterinarian is essential for effective long-term management of toxic neutrophils. Regular communication and collaboration can help ensure that your dog's health is always a top priority.
Conclusion
Toxic neutrophils in dogs are a critical indicator of severe infections or systemic illnesses. Recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and seeking prompt veterinary care can significantly improve your dog's health and quality of life. By staying informed and taking proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition, pet owners can help ensure that their furry companions remain happy and healthy.
We encourage all pet owners to share this article with others and leave comments or questions below. For more information on dog health and wellness, explore our other articles and resources. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of our beloved pets!