In today's digital banking era, understanding the basics of financial systems is essential for everyone. One of the most critical components in banking transactions is the bank routing transit number (RTN). This unique nine-digit code plays a crucial role in ensuring that funds are transferred accurately between banks. Whether you're setting up direct deposits, sending wire transfers, or paying bills online, knowing how RTN works can save you time and money.
A bank routing transit number is not just a random sequence of numbers; it carries significant meaning and serves as a backbone of the banking infrastructure. By learning about RTN, you can better manage your finances and avoid potential errors in transactions.
This article will delve deep into the concept of bank routing transit numbers, exploring their purpose, structure, and applications. You'll also discover tips for finding your RTN and common mistakes to avoid when using it. Let's dive in!
Read also:Ulrike Eidonger A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life Achievements And Legacy
Table of Contents
- What is a Bank Routing Transit Number?
- History of Routing Numbers
- Structure of a Routing Transit Number
- How Does a Routing Transit Number Work?
- Finding Your Bank Routing Transit Number
- Common Uses of Routing Transit Numbers
- Differences Between Routing Transit Numbers and IBAN
- Security and Privacy Concerns with Routing Transit Numbers
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using RT Numbers
- The Future of Routing Transit Numbers
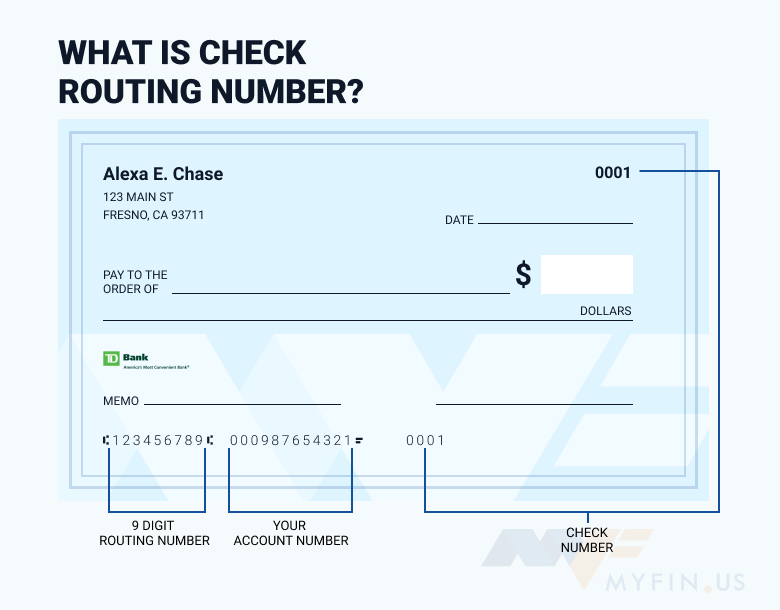
What is a Bank Routing Transit Number?
A bank routing transit number (RTN) is a nine-digit code assigned to financial institutions in the United States. It identifies the specific bank or credit union where an account is held. This number ensures that funds are routed correctly during transactions such as direct deposits, checks, and electronic transfers.
The RTN system was first introduced in 1910 by the American Bankers Association (ABA) to standardize banking processes. Since then, it has become an integral part of the U.S. financial infrastructure.
For example, if you're setting up direct deposit for your paycheck, your employer will require your bank account number and routing transit number to ensure that your salary is deposited into the correct account.
History of Routing Numbers
Development of the ABA Routing Number System
The history of routing numbers dates back to the early 20th century when the banking industry needed a standardized system to process checks efficiently. In 1910, the American Bankers Association (ABA) developed the routing transit number system to address this need.
Initially, routing numbers were used primarily for check processing. Over time, as technology advanced, the system expanded to include electronic funds transfers (EFTs) and other financial transactions.
- 1910: Introduction of the ABA routing number system
- 1940s: Expansion to include electronic processing
- 1990s: Integration with modern banking systems
Structure of a Routing Transit Number
Breaking Down the Nine-Digit Code
A routing transit number consists of nine digits, each with a specific purpose:
Read also:Russian Pushup Benefits A Comprehensive Guide To Maximizing Your Workout
- First four digits: Represent the Federal Reserve Bank district where the financial institution is located.
- Fifth and sixth digits: Indicate the bank's specific Federal Reserve branch.
- Seventh digit: Identifies the type of institution (e.g., commercial bank, savings bank).
- Last two digits: A checksum used to validate the routing number's accuracy.
For instance, the routing number 123456789 can be broken down as follows:
- 1234: Federal Reserve Bank district
- 56: Specific Federal Reserve branch
- 7: Institution type
- 89: Checksum
How Does a Routing Transit Number Work?
When you initiate a transaction, the routing transit number ensures that the funds are sent to the correct financial institution. For example, if you write a check, the RTN on the bottom of the check tells the processing system which bank to contact for verification and settlement.
In electronic transactions, the RTN is used to route the payment request to the appropriate bank. This process happens almost instantly, thanks to modern banking systems and networks like the Automated Clearing House (ACH).
Finding Your Bank Routing Transit Number
Where to Locate Your RT Number
Finding your bank routing transit number is straightforward. Here are some common methods:
- On Your Checks: The RTN is usually printed on the bottom left corner of your checks.
- Bank Statement: Your monthly bank statement may include the routing number.
- Online Banking: Most banks provide the RTN in the account information section of their online platforms.
- Bank's Website: Many banks list their routing numbers on their official websites.
It's important to verify that you're using the correct RTN, as errors can lead to failed transactions or delays.
Common Uses of Routing Transit Numbers
Routing transit numbers are used in various financial transactions, including:
- Direct Deposits: Set up automatic deposits for paychecks, Social Security payments, or other income sources.
- Bill Payments: Pay bills online using your bank account and RTN.
- Wire Transfers: Send or receive funds domestically or internationally.
- ACH Transfers: Transfer money between accounts using the Automated Clearing House network.
Each of these applications relies on accurate routing information to ensure successful transactions.
Differences Between Routing Transit Numbers and IBAN
Comparing U.S. and International Standards
While routing transit numbers are used in the United States, the International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is the global standard for identifying bank accounts. Here are the key differences:
- Scope: RTNs are used only in the U.S., while IBAN is used worldwide.
- Format: RTNs are nine-digit codes, whereas IBANs can vary in length depending on the country.
- Purpose: RTNs primarily identify banks, while IBANs identify both the bank and the specific account.
For international transactions, you may need both an RTN and an IBAN to ensure seamless fund transfers.
Security and Privacy Concerns with Routing Transit Numbers
Protecting Your Financial Information
While routing transit numbers are essential for banking operations, they also pose potential security risks. Sharing your RTN with unauthorized parties could lead to fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized transfers or identity theft.
To safeguard your information:
- Only share your RTN with trusted entities.
- Monitor your accounts regularly for suspicious activity.
- Use secure methods for transmitting sensitive financial data.
Many banks offer additional security features, such as two-factor authentication, to protect your accounts.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using RT Numbers
Ensuring Error-Free Transactions
Errors in routing transit numbers can cause significant delays or even failed transactions. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Using the wrong RTN for domestic vs. international transactions.
- Transposing digits in the nine-digit code.
- Providing outdated or incorrect RTNs.
Double-checking your RTN before initiating any transaction can save you time and frustration.
The Future of Routing Transit Numbers
Adapting to Changing Banking Technologies
As technology continues to evolve, the role of routing transit numbers may change. Emerging innovations, such as blockchain and real-time payment systems, could transform how financial transactions are processed. However, RTNs are likely to remain relevant for the foreseeable future, serving as a foundational element of the U.S. banking system.
Financial institutions are investing in advanced systems to enhance the efficiency and security of RTN-based transactions. These efforts aim to improve customer experience while maintaining the integrity of the financial infrastructure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding bank routing transit numbers is vital for anyone managing their finances in today's digital world. From their historical origins to their modern applications, RTNs play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and secure transactions. By familiarizing yourself with how RTNs work, you can avoid common mistakes and protect your financial information.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your bank's routing transit number and ensuring it's up-to-date. Share this article with friends and family to help them better understand this important aspect of banking. For more insights into personal finance and banking, explore our other resources on the website.
Data sources:
- American Bankers Association (ABA)
- Federal Reserve Bank
- U.S. Treasury Department