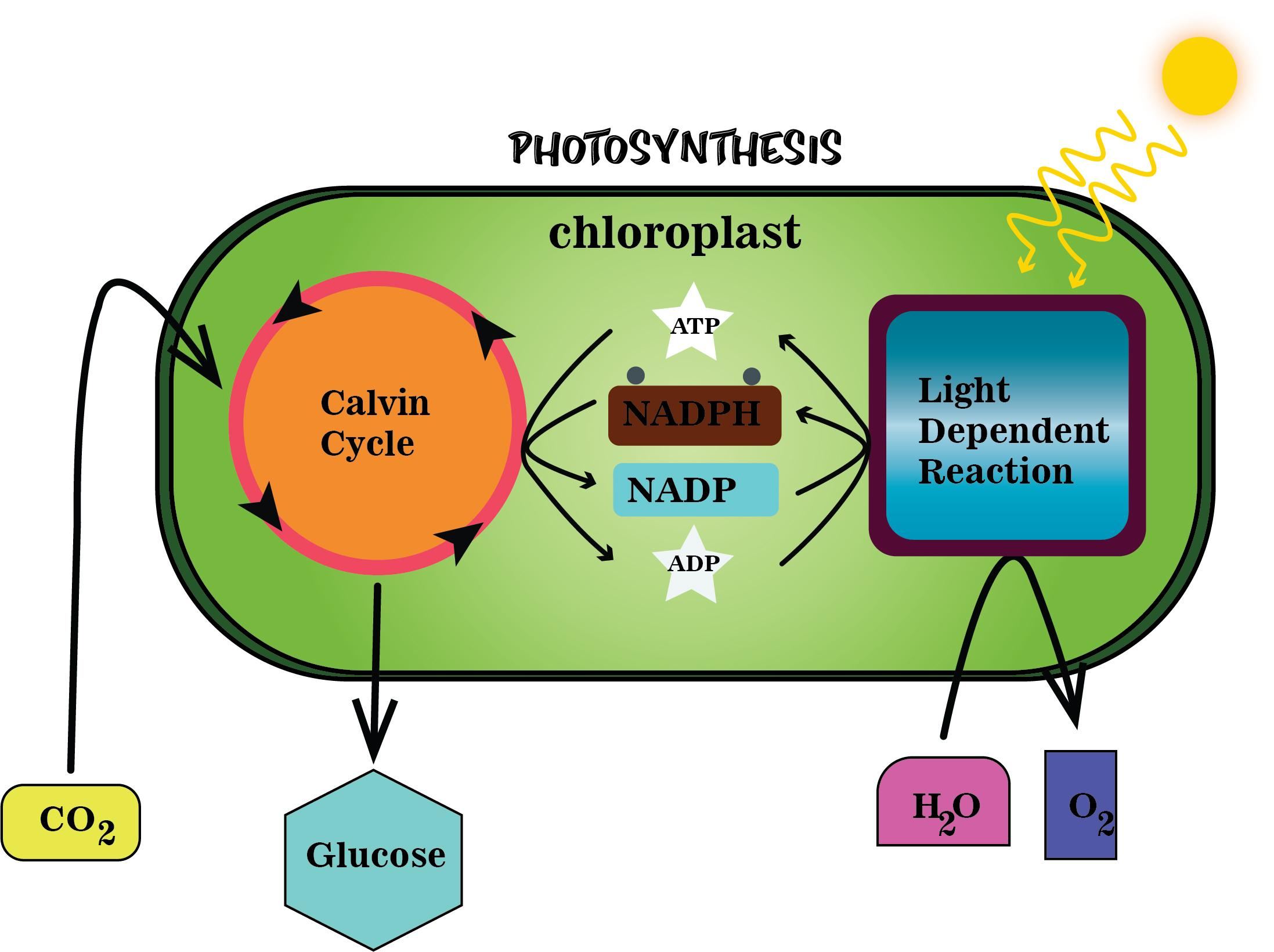
Photosynthesis is one of the most essential biological processes on Earth, and the light-dependent reaction plays a critical role in this energy conversion process. It serves as the starting point where sunlight is harnessed to produce energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH. This process is not only vital for plants but also for the survival of all living organisms that depend on the oxygen and energy it generates.
The light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis is a complex biochemical process that occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. This reaction involves the absorption of light by chlorophyll molecules, leading to the generation of chemical energy. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for anyone interested in plant biology, agriculture, or environmental science.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the light-dependent reaction, exploring its mechanisms, importance, and connection to the overall process of photosynthesis. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about how plants convert sunlight into energy, this guide will provide you with all the information you need.
Read also:Hakeem Jeffries And Wife A Comprehensive Look Into Their Relationship And Life Together
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Photosynthesis
- Location of the Light-Dependent Reaction
- Photosystems in the Light-Dependent Reaction
- The Electron Transport Chain
- Production of ATP and NADPH
- The Role of Water in the Light-Dependent Reaction
- Importance of the Light-Dependent Reaction
- Factors Affecting the Light-Dependent Reaction
- Comparison with Light-Independent Reaction
- Applications in Agriculture
- Conclusion
Introduction to Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules. The process can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reaction and the light-independent reaction (Calvin Cycle). The light-dependent reaction photosynthesis is the first stage and occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
This reaction relies on sunlight to drive the production of ATP and NADPH, which are essential for the subsequent stages of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll, the primary pigment involved in this process, absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy through a series of complex biochemical reactions.
Why is Photosynthesis Important?
Photosynthesis is the foundation of life on Earth. It produces oxygen, which is essential for the survival of most organisms, and provides energy in the form of glucose. This process also plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Location of the Light-Dependent Reaction
The light-dependent reaction photosynthesis takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. These membranes are stacked in structures called grana and contain pigments such as chlorophyll, which are responsible for capturing light energy. The thylakoid membranes are also the site of the electron transport chain and ATP synthase, which are essential components of this reaction.
Structure of Chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells.
- They contain thylakoid membranes, where the light-dependent reaction occurs.
- The stroma, the fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoids, is where the Calvin Cycle takes place.
Photosystems in the Light-Dependent Reaction
The light-dependent reaction involves two main photosystems: Photosystem I (PSI) and Photosystem II (PSII). These photosystems work together to capture light energy and drive the electron transport chain. PSII is responsible for splitting water molecules, while PSI generates NADPH through a process called cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Key Components of Photosystems
- Reaction centers: Contain chlorophyll molecules that absorb light energy.
- Antenna complexes: Help capture light energy and transfer it to the reaction centers.
- Primary electron acceptors: Capture excited electrons from the reaction centers.
The Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes embedded in the thylakoid membranes. It plays a crucial role in the light-dependent reaction photosynthesis by transferring electrons from PSII to PSI, generating a proton gradient that drives ATP production.
Read also:Jayne Modean The Ultimate Guide To Her Life Career And Achievements
Steps in the Electron Transport Chain
- Excited electrons are transferred from PSII to the first protein complex.
- These electrons are passed through a series of carriers, including plastoquinone and cytochrome b6f complex.
- Finally, the electrons reach PSI, where they are re-energized by light and transferred to NADP+ to form NADPH.
Production of ATP and NADPH
ATP and NADPH are the two main products of the light-dependent reaction. ATP is generated through a process called chemiosmosis, where the proton gradient created by the electron transport chain drives ATP synthase to produce ATP. NADPH, on the other hand, is formed when electrons from PSI reduce NADP+.
Why Are ATP and NADPH Important?
ATP and NADPH are essential for the Calvin Cycle, where carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules. These energy carriers ensure that the plant has the resources needed to produce glucose and other organic compounds.
The Role of Water in the Light-Dependent Reaction
Water plays a critical role in the light-dependent reaction photosynthesis. During this process, water molecules are split into protons, electrons, and oxygen. The electrons are used to replace those lost by PSII, while the protons contribute to the proton gradient. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of this reaction.
Water Splitting Process
- Oxygen-evolving complex (OEC): Responsible for splitting water molecules.
- Protons are used in the electron transport chain to create a proton gradient.
- Oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct.
Importance of the Light-Dependent Reaction
The light-dependent reaction is essential for the overall process of photosynthesis. It provides the energy carriers (ATP and NADPH) necessary for the Calvin Cycle, ensuring that plants can produce glucose and other organic compounds. Additionally, this reaction is responsible for producing oxygen, which is vital for the survival of aerobic organisms.
Environmental Impact
By producing oxygen and removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, the light-dependent reaction helps regulate the Earth's climate. This process is particularly important in combating global warming and maintaining ecological balance.
Factors Affecting the Light-Dependent Reaction
Several factors can influence the efficiency of the light-dependent reaction photosynthesis. These include light intensity, temperature, water availability, and the concentration of carbon dioxide.
Optimizing Light-Dependent Reaction
- Light intensity: Higher light intensity generally increases the rate of the reaction, up to a certain point.
- Temperature: Optimal temperature ensures that enzymes involved in the reaction function efficiently.
- Water availability: Adequate water supply is crucial for the splitting of water molecules.
Comparison with Light-Independent Reaction
While the light-dependent reaction relies on sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH, the light-independent reaction (Calvin Cycle) uses these energy carriers to fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules. The two stages of photosynthesis are interconnected and work together to ensure the efficient production of glucose.
Key Differences
- Location: Light-dependent reaction occurs in thylakoid membranes, while light-independent reaction occurs in the stroma.
- Energy Source: Light-dependent reaction uses sunlight, while light-independent reaction uses ATP and NADPH.
Applications in Agriculture
Understanding the light-dependent reaction photosynthesis has significant implications for agriculture. By optimizing factors such as light intensity, temperature, and water availability, farmers can enhance crop productivity and improve food security. Additionally, research into photosynthesis can lead to the development of more efficient crops that can thrive in challenging environments.
Future Directions
Scientists are exploring ways to enhance photosynthetic efficiency through genetic engineering and other biotechnological approaches. These innovations could revolutionize agriculture and help address global food shortages.
Conclusion
The light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis is a fascinating and essential process that powers life on Earth. By understanding its mechanisms and importance, we can appreciate the intricate ways in which nature converts sunlight into energy. Whether you're studying plant biology, agriculture, or environmental science, this knowledge can inspire further exploration and innovation.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may find it interesting. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below. For more insights into photosynthesis and related topics, explore our other articles on this site.
References:
- Alberts, B., et al. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Science.
- Biochemistry, 5th Edition. Berg, J.M., Tymoczko, J.L., & Stryer, L. (2002). W.H. Freeman and Company.
- National Geographic. (2023). The Role of Photosynthesis in Ecosystems.