Light dependent definition refers to the processes or mechanisms that rely on the presence of light to function effectively. Whether in the realms of biology, physics, or technology, understanding light-dependent processes is crucial for numerous applications and scientific studies. In this article, we'll delve deep into what it means to be light-dependent, explore its applications, and discuss its significance in various fields.
Light is one of the most fundamental elements in nature, driving processes like photosynthesis, enabling vision, and powering countless technological advancements. When we talk about light-dependent phenomena, we refer to how light influences biological, chemical, and physical systems. This article will explore the intricacies of light-dependent processes, their importance, and how they impact our daily lives.
Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply someone curious about the science behind light-dependent mechanisms, this article will provide comprehensive insights into the subject. Let's dive into the fascinating world of light-dependent processes and their applications.
Read also:Pelvic Floor Therapy Benefits Unlocking The Secrets To A Stronger Healthier You
Table of Contents
- Light Dependent Definition in Biological Context
- The Role of Light in Photosynthesis
- Light Dependent Definition in Physics
- Technological Applications of Light-Dependent Processes
- Light Dependence in Solar Energy
- Bioluminescence: Nature's Light-Dependent Phenomenon
- Health Implications of Light Dependence
- Environmental Impact of Light-Dependent Technologies
- Scientific Research on Light-Dependent Mechanisms
- Conclusion and Future Prospects
Light Dependent Definition in Biological Context
In biology, light-dependent processes are essential for sustaining life on Earth. These processes occur in organisms ranging from plants to algae and even certain bacteria. At the core of these mechanisms is the ability to convert light energy into chemical energy, which fuels biological functions.
Photosynthesis is perhaps the most well-known example of a light-dependent biological process. Plants use sunlight to produce glucose, a critical energy source for cellular respiration. This process not only supports plant life but also contributes to the oxygen supply in the atmosphere, making it vital for all aerobic organisms.
Beyond photosynthesis, light plays a role in regulating circadian rhythms in animals and humans. Light exposure influences sleep patterns, hormone production, and overall well-being. Understanding these mechanisms can lead to advancements in medicine and health care.
Key Features of Biological Light Dependence
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
- Role in regulating biological rhythms
- Impact on ecological systems
The Role of Light in Photosynthesis
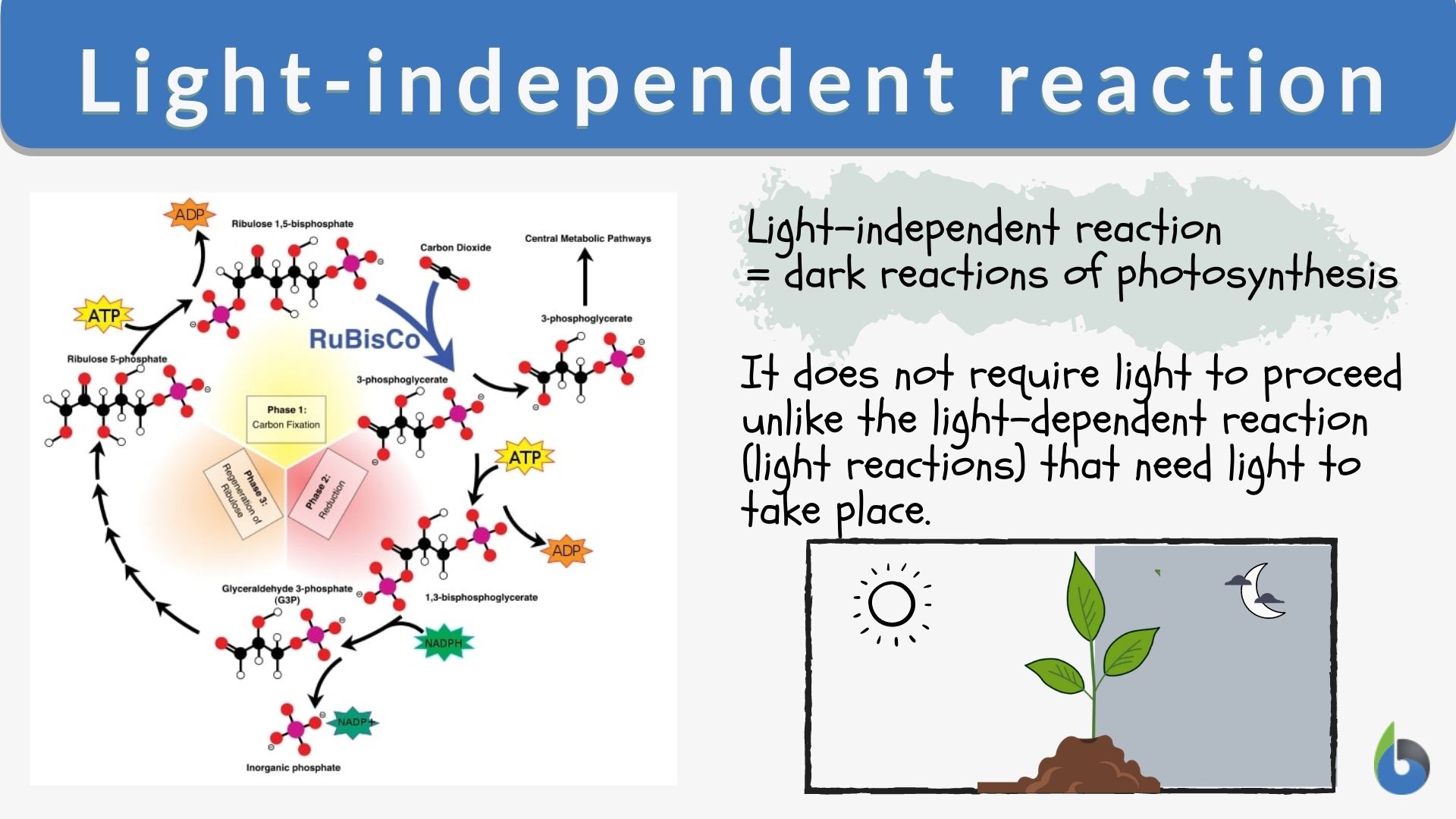
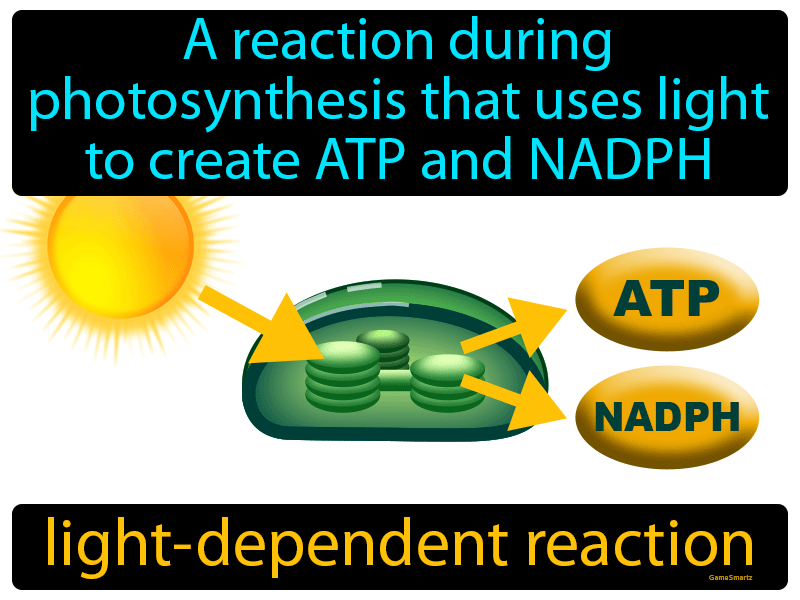
Photosynthesis is a light-dependent definition that exemplifies the importance of light in biological systems. This process occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle). The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involve the absorption of sunlight by chlorophyll molecules.
During these reactions, light energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons. The electrons are then transferred through an electron transport chain, generating ATP and NADPH—energy carriers essential for the Calvin cycle.
Without light, the initial reactions cannot occur, highlighting the dependency of photosynthesis on sunlight. This interdependence underscores the significance of light in sustaining plant life and, by extension, the entire food chain.
Read also:Exploring Ana De Armas Ethnicity A Deep Dive Into Her Heritage And Background
Steps in Light-Dependent Reactions
- Light absorption by chlorophyll
- Water splitting (photolysis)
- Electron transport and ATP synthesis
Light Dependent Definition in Physics
In the field of physics, light-dependent processes revolve around the interaction of light with matter. These interactions include absorption, reflection, refraction, and emission, all of which are governed by the principles of quantum mechanics and electromagnetism.
One notable example is the photoelectric effect, where light of sufficient energy causes the emission of electrons from a material's surface. This phenomenon was pivotal in the development of quantum theory and has practical applications in devices like solar panels and photodetectors.
Another important light-dependent process is luminescence, which involves the emission of light by a substance after it absorbs photons. This property is utilized in fluorescent lighting and other technological innovations.
Applications of Light-Dependent Physics
- Photovoltaic cells for solar energy
- Fluorescent and LED lighting
- Photodetectors in cameras and sensors
Technological Applications of Light-Dependent Processes
The integration of light-dependent mechanisms into technology has revolutionized various industries. From renewable energy to communication systems, light plays a central role in modern innovation. For instance, fiber optic cables rely on the transmission of light signals to deliver high-speed internet across vast distances.
Solar panels are another prominent example of light-dependent technology. By harnessing sunlight, these panels convert light energy into electricity, providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Advances in photovoltaic technology continue to improve efficiency and reduce costs, making solar energy more accessible worldwide.
In the realm of healthcare, light-dependent therapies such as photodynamic therapy (PDT) are used to treat cancer and other conditions. These treatments involve the activation of light-sensitive drugs by specific wavelengths of light, targeting diseased cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
Emerging Technologies
- Quantum dots for advanced displays
- Optogenetics in neuroscience research
- Light-based communication systems
Light Dependence in Solar Energy
Solar energy is a prime example of a light-dependent technology that addresses global energy challenges. By capturing sunlight, solar panels generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This renewable energy source reduces reliance on fossil fuels and mitigates environmental impacts associated with traditional power generation.
Efficiency improvements in solar technology have been driven by advancements in materials science and engineering. Innovations such as perovskite solar cells and bifacial panels enhance energy conversion rates, making solar power more viable for widespread adoption.
Government incentives and decreasing costs have also contributed to the growth of the solar industry. As awareness of climate change increases, the demand for clean energy solutions like solar power continues to rise.
Challenges in Solar Energy
- Intermittency of sunlight
- Energy storage limitations
- High initial installation costs
Bioluminescence: Nature's Light-Dependent Phenomenon
Bioluminescence is a fascinating example of light-dependent processes in nature. This phenomenon occurs when living organisms emit light through chemical reactions within their bodies. Bioluminescent creatures, such as fireflies, jellyfish, and certain deep-sea fish, use this ability for communication, attracting mates, and deterring predators.
Scientific research into bioluminescence has led to significant breakthroughs in biotechnology. Green fluorescent protein (GFP), derived from jellyfish, is widely used in genetic engineering and medical imaging. By tagging proteins with GFP, researchers can visualize cellular processes and study disease mechanisms at the molecular level.
The study of bioluminescence also provides insights into evolutionary biology and ecological interactions, enriching our understanding of the natural world.
Uses of Bioluminescence in Science
- Genetic engineering and gene expression studies
- Medical imaging and diagnostics
- Environmental monitoring
Health Implications of Light Dependence
Light has profound effects on human health, influencing both physical and mental well-being. Exposure to natural light regulates circadian rhythms, affecting sleep patterns, mood, and cognitive function. Conversely, inadequate or irregular light exposure can lead to conditions such as seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and insomnia.
UV light, while beneficial in moderate amounts for vitamin D synthesis, poses risks when overexposed. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can cause skin damage, premature aging, and increase the likelihood of skin cancer. Balancing light exposure is therefore crucial for maintaining optimal health.
Light therapy is an emerging treatment for various health issues, including depression, sleep disorders, and certain skin conditions. By mimicking natural sunlight, light therapy devices help regulate biological processes and improve overall well-being.
Health Benefits of Light Exposure
- Vitamin D synthesis
- Improved mood and cognitive function
- Regulation of circadian rhythms
Environmental Impact of Light-Dependent Technologies
While light-dependent technologies offer numerous benefits, they also raise environmental concerns. The production and disposal of solar panels, for instance, involve the use of hazardous materials and energy-intensive processes. Ensuring sustainable practices throughout the lifecycle of these technologies is essential for minimizing ecological harm.
Light pollution is another issue associated with artificial lighting. Excessive or misdirected light disrupts ecosystems, affecting wildlife behavior and migration patterns. Implementing energy-efficient lighting solutions and smart urban planning can help mitigate these impacts.
As the world transitions toward renewable energy sources, addressing the environmental challenges of light-dependent technologies will be critical for achieving long-term sustainability.
Solutions for Environmental Challenges
- Recycling programs for solar panels
- Energy-efficient lighting systems
- Smart city initiatives to reduce light pollution
Scientific Research on Light-Dependent Mechanisms
Ongoing scientific research continues to uncover new insights into light-dependent processes. Advances in nanotechnology, quantum mechanics, and synthetic biology are expanding the possibilities for harnessing light in innovative ways. For example, researchers are exploring the use of light-activated materials for drug delivery and cancer treatment.
Collaboration between disciplines such as physics, biology, and engineering drives progress in this field. Interdisciplinary approaches enable the development of novel technologies and therapies that leverage the unique properties of light.
As our understanding of light-dependent mechanisms deepens, so too does our ability to address global challenges in energy, health, and the environment.
Future Directions in Research
- Light-based quantum computing
- Artificial photosynthesis for clean energy
- Optogenetic tools for neurological disorders
Conclusion and Future Prospects
In conclusion, the light-dependent definition encompasses a wide range of processes that are integral to life, technology, and science. From the biological marvels of photosynthesis to the technological innovations of solar energy, light-dependent mechanisms shape our world in profound ways. Understanding these processes not only enhances our knowledge but also opens doors to sustainable solutions for global challenges.
We invite you to explore further by engaging with the content, sharing your thoughts in the comments, or delving into related articles on our site. Together, we can illuminate the path toward a brighter future powered by light-dependent innovations.
.PNG)