Islam and Muslims are often discussed together, yet they represent distinct concepts that are vital to understanding the religion and its followers. Exploring the differences between Islam and Muslims provides a clearer picture of the faith, its practices, and its adherents. In this article, we will delve into these distinctions and shed light on the nuances that define them.
Understanding the differences between Islam and Muslims is essential for fostering mutual respect and tolerance in a globalized world. Misconceptions often arise due to a lack of knowledge, leading to stereotypes and biases. By exploring the core aspects of Islam and the diverse ways Muslims practice their faith, we aim to bridge gaps and promote a deeper understanding.
This article will cover various aspects of the topic, including historical context, cultural diversity, religious practices, and contemporary issues. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the subject, this guide will provide valuable insights into the distinctions between Islam and its followers.
Read also:Seong Jae Gyeong 50 Years Old A Comprehensive Look At The Life Achievements And Legacy
Table of Contents
- Overview of Islam
- Who Are Muslims?
- Core Beliefs of Islam
- Islamic Practices
- Cultural Diversity Among Muslims
- Common Misconceptions About Islam and Muslims
- Historical Context of Islam
- Contemporary Issues in the Muslim World
- Scholarly Perspectives on Muslim Islam Differences
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Overview of Islam
Islam is one of the world's major religions, with over 1.9 billion adherents globally. The word "Islam" means "submission" in Arabic, signifying the submission to the will of Allah (God). It is a monotheistic faith that originated in the Arabian Peninsula in the 7th century CE with the teachings of Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him).
Foundations of Islam
The foundation of Islam lies in the Quran, which Muslims believe to be the literal word of God revealed to Prophet Muhammad. Alongside the Quran, the Hadith (sayings and actions of the Prophet) serves as a guiding principle for Muslims in their daily lives. Together, these texts form the core of Islamic teachings.
Five Pillars of Islam
- Shahada: Declaration of faith in the oneness of God and the prophethood of Muhammad.
- Salat: Performing five daily prayers.
- Zakat: Giving alms to the poor and needy.
- Sawm: Fasting during the month of Ramadan.
- Hajj: Pilgrimage to Mecca, required once in a lifetime for those who are able.
Who Are Muslims?
Muslims are individuals who follow the teachings of Islam. They come from diverse cultural, ethnic, and national backgrounds, making the Muslim community one of the most varied religious groups in the world. While they share common beliefs and practices, the ways in which they express their faith can differ significantly depending on their environment and traditions.
Read also:Keith Bynum The Journey Achievements And Legacy
Demographics of Muslims
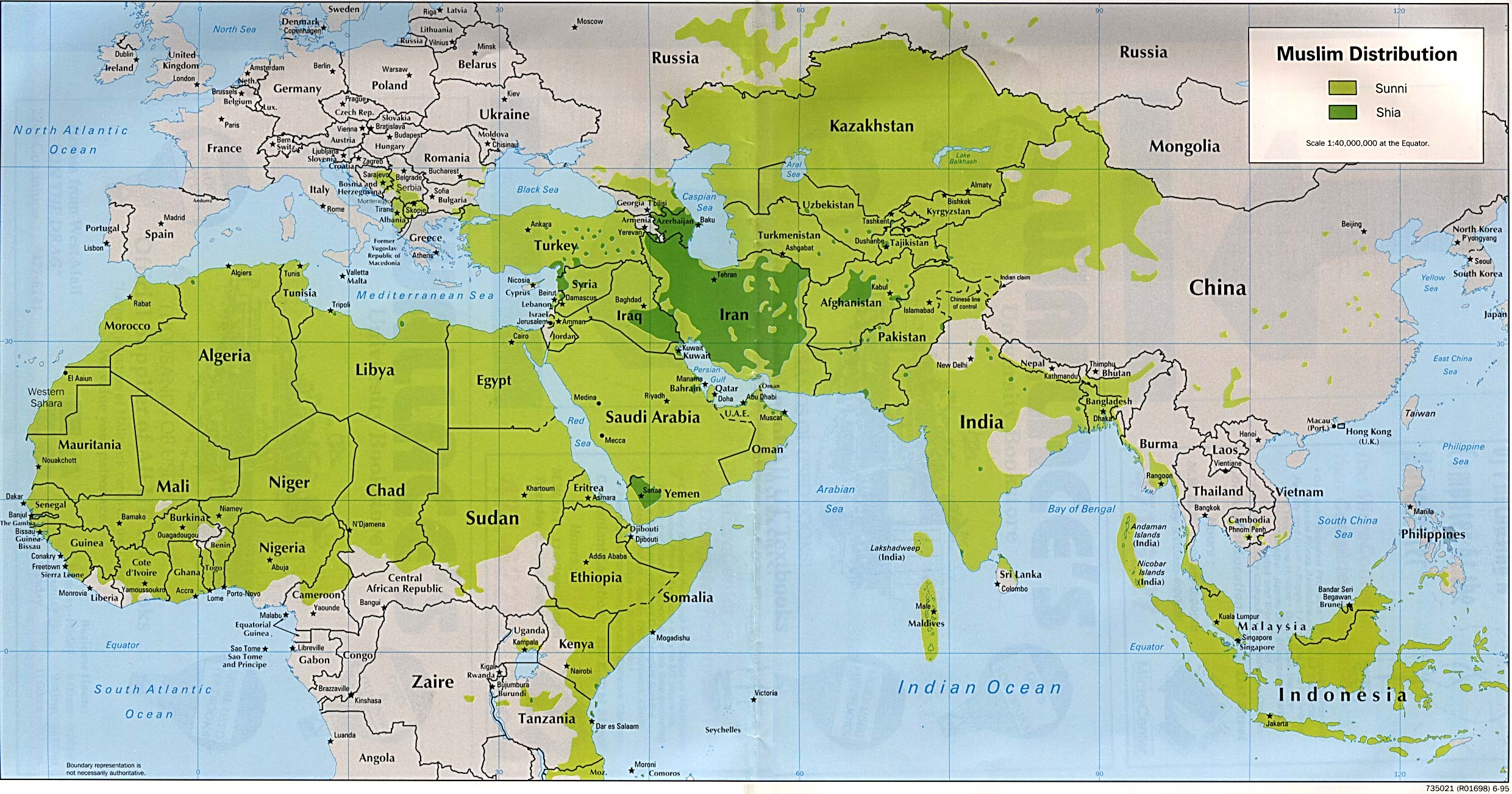
According to the Pew Research Center, the majority of Muslims live in Asia-Pacific, followed by the Middle East and North Africa. Indonesia has the largest Muslim population, while countries like India, Pakistan, and Nigeria also have significant Muslim communities. This global distribution highlights the cultural richness and diversity within the Muslim world.
Core Beliefs of Islam
The core beliefs of Islam revolve around the concept of Tawhid, or the oneness of God. Muslims believe in the existence of angels, prophets, holy scriptures, and the Day of Judgment. These beliefs shape their worldview and guide their actions in accordance with divine commandments.
Key Islamic Beliefs
- Belief in One God: Muslims worship Allah, the creator and sustainer of the universe.
- Prophethood: Recognition of all prophets, including Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and Muhammad.
- Revelation: Acceptance of holy scriptures such as the Torah, Psalms, Gospel, and Quran.
- Life After Death: Faith in the resurrection and accountability on the Day of Judgment.
Islamic Practices
Islamic practices encompass a wide range of rituals and customs that reflect the faith's teachings. From daily prayers to charitable acts, these practices reinforce the spiritual connection between Muslims and their Creator.
Prayer and Worship
Salat, or prayer, is a fundamental aspect of Islamic practice. Muslims perform five daily prayers at specific times, facing the Kaaba in Mecca. These prayers serve as a constant reminder of their devotion and commitment to God.
Cultural Diversity Among Muslims
While Islam provides a unifying framework for its followers, cultural diversity plays a significant role in shaping how Muslims practice their faith. From traditional clothing to festive celebrations, the variations within the Muslim world reflect its global reach and adaptability.
Cultural Practices
- Hijab: The wearing of headscarves by Muslim women as an expression of modesty.
- Eid Celebrations: Festive occasions like Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha bring families and communities together in joyous celebration.
- Cuisine: Islamic dietary laws influence the preparation and consumption of food, with halal practices ensuring compliance with religious guidelines.
Common Misconceptions About Islam and Muslims
Misconceptions about Islam and Muslims often stem from stereotypes perpetuated by media and societal biases. Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for promoting accurate representations and fostering understanding.
Myths vs. Reality
- Violence and Terrorism: Contrary to stereotypes, the vast majority of Muslims condemn violence and terrorism as contrary to Islamic teachings.
- Women's Rights: Islam emphasizes the equality and dignity of women, with practices like hijab being a personal choice rather than a form of oppression.
- Sharia Law: Sharia is a comprehensive legal framework that addresses various aspects of life, but its interpretation varies across cultures and contexts.
Historical Context of Islam
Understanding the historical context of Islam provides valuable insights into its development and spread. From the early days of Prophet Muhammad's mission to the expansion of the Islamic empire, the religion has undergone significant transformations that continue to influence its followers today.
Key Historical Events
- Hijra: The migration of Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE marks the beginning of the Islamic calendar.
- Conquests and Expansion: The rapid spread of Islam through military campaigns and trade routes established a vast empire encompassing diverse regions.
- Golden Age of Islam: A period of intellectual and cultural flourishing during which Muslim scholars made significant contributions to science, philosophy, and the arts.
Contemporary Issues in the Muslim World
The modern Muslim world faces a range of challenges, including political instability, economic disparities, and social issues. Addressing these concerns requires collective efforts from both Muslim communities and the global society at large.
Current Challenges
- Radicalization: Combating extremist ideologies that distort Islamic teachings.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Promoting understanding and cooperation between Muslims and followers of other religions.
- Human Rights: Advocating for justice and equality in Muslim-majority countries and beyond.
Scholarly Perspectives on Muslim Islam Differences
Academic research and scholarly perspectives offer valuable insights into the distinctions between Islam and Muslims. Experts in the field analyze the complexities of the religion and its followers, providing nuanced interpretations that enrich our understanding.
Notable Scholars
- Professor Seyyed Hossein Nasr: A prominent Islamic philosopher whose works explore the spiritual dimensions of Islam.
- Dr. Tariq Ramadan: A contemporary thinker who addresses the challenges facing Muslims in the modern world.
- Professor John Esposito: A leading authority on Islam and its relationship with the West.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the differences between Islam and Muslims is essential for promoting harmony and respect in an increasingly interconnected world. By exploring the core beliefs, practices, and cultural diversity within the Muslim community, we can dispel misconceptions and foster meaningful dialogue.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website that delve into related topics. Together, let's continue the conversation and work towards a more informed and compassionate society.
References:
- Pew Research Center. (2021). The Future of World Religions: Population Growth Projections, 2010-2050.
- Nasr, S. H. (2002). The Heart of Islam: Enduring Values for Humanity. HarperOne.
- Esposito, J. L. (2002). Unholy War: Terror in the Name of Islam. Oxford University Press.