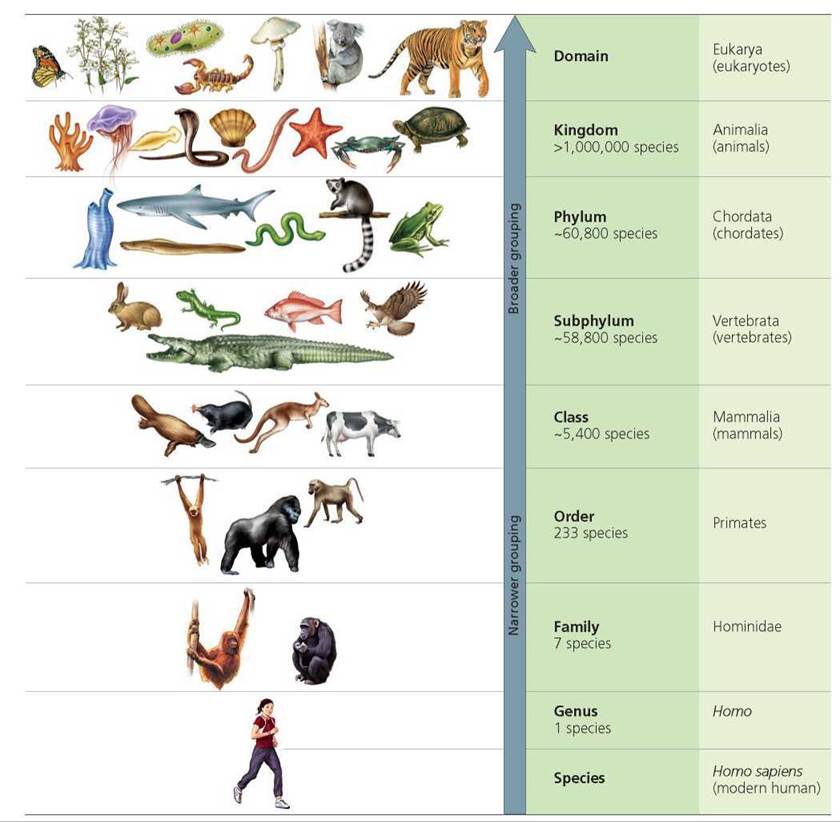
Kingdom Class Phylum Order is a fundamental concept in biological classification that helps organize living organisms systematically. This hierarchical system allows scientists to categorize and understand the vast diversity of life on Earth. By delving into this topic, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between species.
The classification system is not just a theoretical framework; it has practical applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. By understanding how organisms are classified, we can better comprehend their ecological roles and evolutionary histories.
In this article, we will explore the concept of Kingdom Class Phylum Order in detail, breaking it down into manageable sections to ensure clarity and comprehension. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about biology, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of biological taxonomy.
Read also:Boost Your Website Ranking Position The Ultimate Guide For Success
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Kingdom Class Phylum Order
- History of Biological Classification
- Understanding Kingdom
- What is Phylum?
- The Role of Class in Classification
- Exploring the Order
- Family in Taxonomy
- Genus and Species
- Examples of Kingdom Class Phylum Order
- Importance of Biological Classification
- Challenges in Modern Classification
Introduction to Kingdom Class Phylum Order
The biological classification system is a structured framework used to categorize living organisms based on shared characteristics. At the core of this system lies the hierarchy: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. Each level provides a more specific description of an organism's characteristics, enabling scientists to study and compare different species effectively.
The concept of Kingdom Class Phylum Order is rooted in the work of early taxonomists like Carl Linnaeus, who laid the foundation for modern taxonomy. This system has evolved over time to incorporate new discoveries and advancements in genetic research, ensuring its relevance in contemporary science.
History of Biological Classification
The history of biological classification dates back to ancient civilizations, where early philosophers attempted to categorize living organisms based on observable traits. However, it was Carl Linnaeus who revolutionized the field with his binomial nomenclature system in the 18th century. Linnaeus's work provided a standardized method for naming and classifying species, which remains the basis of modern taxonomy.
Key Milestones in Classification History
- Aristotle's classification system based on physical characteristics.
- Carl Linnaeus's introduction of binomial nomenclature in 1753.
- The discovery of DNA and its role in genetic classification.
These milestones highlight the evolution of biological classification from a descriptive science to a data-driven field that incorporates molecular biology and genetics.
Understanding Kingdom
The Kingdom is the highest rank in the biological classification system, representing the broadest category of organisms. There are traditionally five kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. However, modern taxonomy often uses a six-kingdom system that includes Archaea as a separate category.
Characteristics of Each Kingdom
- Monera: Single-celled organisms without a nucleus, such as bacteria.
- Protista: Single-celled or simple multicellular organisms, including algae and protozoa.
- Fungi: Multicellular organisms that obtain nutrients through absorption, such as mushrooms and molds.
- Plantae: Multicellular organisms capable of photosynthesis, including trees and flowers.
- Animalia: Multicellular organisms that obtain nutrients through ingestion, such as mammals and insects.
- Archaea: Single-celled organisms with unique genetic and biochemical properties.
What is Phylum?
Phylum is the second rank in the biological classification system, representing a more specific grouping of organisms within a kingdom. For example, in the Animalia kingdom, phyla include Chordata (vertebrates) and Arthropoda (insects and crustaceans). Each phylum is defined by a set of shared characteristics that distinguish it from others.
Read also:Somalia Girls Telegram A Comprehensive Guide
Examples of Phyla in the Animal Kingdom
- Chordata: Includes vertebrates such as mammals, birds, and fish.
- Arthropoda: Includes insects, spiders, and crustaceans.
- Mollusca: Includes snails, clams, and octopuses.
Phyla provide a more detailed understanding of the diversity within each kingdom, allowing scientists to study evolutionary relationships between organisms.
The Role of Class in Classification
Class is the third rank in the biological classification system, further dividing organisms within a phylum based on shared characteristics. For example, the class Mammalia within the phylum Chordata includes all mammals, while the class Insecta within the phylum Arthropoda includes all insects.
Characteristics of Classes
- Mammalia: Warm-blooded vertebrates with hair or fur and mammary glands.
- Insecta: Invertebrates with three body segments and six legs.
- Aves: Warm-blooded vertebrates with feathers and wings.
Classes provide a more specific framework for studying the traits and behaviors of organisms within a phylum.
Exploring the Order
Order is the fourth rank in the biological classification system, offering an even more detailed categorization of organisms within a class. For example, the order Carnivora within the class Mammalia includes predators such as lions and wolves, while the order Primates includes humans and apes.
Significance of Orders
- Orders help scientists identify evolutionary relationships between species.
- They provide insights into the ecological roles of organisms within a class.
- Orders often share specific anatomical or behavioral traits that distinguish them from others.
Family in Taxonomy
Family is the fifth rank in the biological classification system, representing a more specific grouping of organisms within an order. For example, the family Felidae within the order Carnivora includes all cats, while the family Hominidae within the order Primates includes humans and great apes.
Characteristics of Families
- Felidae: Includes all species of cats, both domestic and wild.
- Hominidae: Includes humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans.
- Canidae: Includes dogs, wolves, and foxes.
Families allow for a more nuanced understanding of the relationships between species, making it easier to study their evolutionary histories.
Genus and Species
Genus and species are the final two ranks in the biological classification system, representing the most specific categories of organisms. The genus is a group of closely related species, while the species is the basic unit of classification, representing a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
Examples of Genus and Species
- Homo sapiens: The genus Homo includes modern humans and extinct species like Homo neanderthalensis.
- Panthera leo: The genus Panthera includes lions, tigers, and leopards, while the species leo specifically refers to lions.
- Canis lupus: The genus Canis includes wolves, dogs, and coyotes, while the species lupus refers to gray wolves.
Genus and species provide the most detailed level of classification, enabling scientists to study the unique traits and behaviors of individual organisms.
Examples of Kingdom Class Phylum Order
Understanding Kingdom Class Phylum Order is best achieved through examples that illustrate how the system works in practice. Below are some examples of organisms classified using this hierarchical system:
Example 1: Panthera leo (Lion)
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Felidae
- Genus: Panthera
- Species: leo
Example 2: Homo sapiens (Human)
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
- Family: Hominidae
- Genus: Homo
- Species: sapiens
These examples demonstrate how the classification system provides a comprehensive framework for organizing and understanding the diversity of life on Earth.
Importance of Biological Classification
The biological classification system is essential for organizing and understanding the vast diversity of life on Earth. By providing a standardized framework for categorizing organisms, it enables scientists to study evolutionary relationships, ecological roles, and conservation needs. Furthermore, classification plays a critical role in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and environmental science, where accurate identification of species is crucial.
Applications of Classification
- Medicine: Identifying pathogens and developing treatments for diseases.
- Agriculture: Classifying crops and livestock for breeding and management.
- Conservation: Protecting endangered species and preserving biodiversity.
Without a systematic approach to classification, the study of biology would be far more challenging and less effective.
Challenges in Modern Classification
While the biological classification system has proven invaluable, it faces challenges in the modern era. Advances in genetic research have revealed complexities in the relationships between organisms that traditional classification methods may not fully capture. Additionally, the discovery of new species and the reclassification of existing ones require constant updates to the system.
Addressing Modern Challenges
- Incorporating genetic data into classification systems.
- Developing computational tools to analyze large datasets.
- Collaborating with scientists across disciplines to refine classification methods.
By addressing these challenges, scientists can ensure that the biological classification system remains a robust and effective tool for understanding life on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of Kingdom Class Phylum Order provides a fundamental framework for organizing and understanding the diversity of life on Earth. By exploring the history, components, and applications of this classification system, we gain valuable insights into the relationships between organisms and their evolutionary histories. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about biology, this guide has hopefully provided a comprehensive overview of the topic.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on related topics. Together, we can deepen our understanding of the fascinating world of biological taxonomy.