Bank transit numbers play a crucial role in banking operations, especially when it comes to transferring funds between accounts. If you've ever wondered what a bank transit number is and how it works, you're not alone. Many people find themselves puzzled by the terminology used in banking systems. In this article, we'll break down everything you need to know about bank transit numbers.
A bank transit number is a unique identifier assigned to financial institutions to streamline transactions and ensure accurate routing of funds. This number acts as a digital address, allowing banks to identify where money is coming from and where it needs to go. Understanding this concept is essential for anyone who engages in financial transactions, whether personal or business-related.
Throughout this article, we'll explore the definition, purpose, and application of bank transit numbers. We'll also delve into common questions and provide practical tips to help you use this information effectively. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how bank transit numbers work and why they are important in modern banking.
Read also:Does Bill Oreilly Have A Wife A Comprehensive Look Into His Personal Life
Table of Contents
- What is a Bank Transit Number?
- Why is a Bank Transit Number Important?
- Understanding the Format of a Bank Transit Number
- Types of Bank Transit Numbers
- How to Find Your Bank Transit Number
- Common Uses of Bank Transit Numbers
- Differences Between Bank Transit Numbers and Routing Numbers
- Security Concerns with Bank Transit Numbers
- The History of Bank Transit Numbers
- Tips for Managing Bank Transit Numbers
What is a Bank Transit Number?
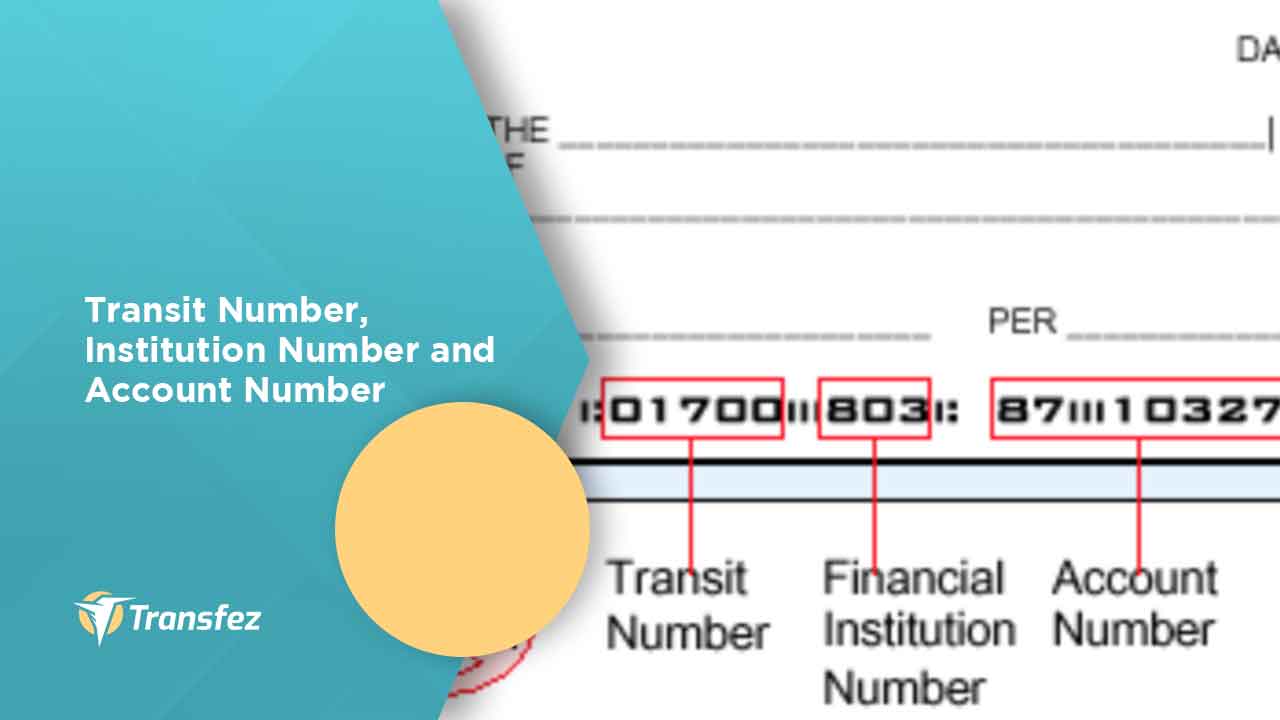
A bank transit number, also known as a routing transit number (RTN) in some regions, is a nine-digit code that identifies a specific financial institution within a banking system. This number is primarily used in the United States and Canada to facilitate the movement of funds between banks and credit unions. It ensures that money is routed to the correct institution and account.
In Canada, the bank transit number typically consists of five digits representing the branch and three digits representing the financial institution. Together, these digits form a unique identifier that is critical for domestic transactions. In the U.S., the routing transit number follows a standardized nine-digit format, which includes a check digit for validation purposes.
Understanding the structure of a bank transit number is essential for anyone who engages in electronic fund transfers, direct deposits, or bill payments. These numbers are designed to minimize errors and ensure that transactions are processed efficiently and securely.
How Does a Bank Transit Number Work?
When you initiate a transaction, such as a direct deposit or an electronic fund transfer, the bank transit number is used to verify the originating and receiving institutions. This process ensures that the funds are routed to the correct bank or credit union. Without a valid bank transit number, transactions may fail or be delayed.
Why is a Bank Transit Number Important?
A bank transit number serves as a critical component of the banking system, ensuring that financial transactions are executed accurately and efficiently. Its importance lies in its ability to:
Read also:Did George Jung Ever See His Daughter Again The Untold Story
- Identify specific financial institutions and branches
- Facilitate secure and reliable fund transfers
- Minimize errors in transaction processing
- Support automated clearing house (ACH) operations
For businesses and individuals alike, having the correct bank transit number is crucial for maintaining smooth financial operations. Whether you're setting up direct deposits, paying bills online, or transferring money between accounts, this number plays a vital role in ensuring that your transactions are processed correctly.
Understanding the Format of a Bank Transit Number
The format of a bank transit number varies slightly depending on the country and banking system. In Canada, the transit number is composed of:
- Five digits representing the branch number
- Three digits representing the financial institution number
In the United States, the routing transit number follows a standardized nine-digit format:
- Four digits identifying the Federal Reserve Bank
- Four digits identifying the financial institution
- One check digit for validation
This standardized format ensures consistency across the banking industry, making it easier for institutions to process transactions efficiently.
Breaking Down the Components
Each digit in a bank transit number has a specific purpose. For example, in the U.S. routing transit number, the first four digits indicate the Federal Reserve Bank responsible for processing the transaction. The next four digits identify the financial institution, while the final digit serves as a checksum to verify the validity of the number.
Types of Bank Transit Numbers
Bank transit numbers can be categorized into different types based on their function and usage. The most common types include:
- Routing Transit Numbers (RTNs): Used primarily in the United States for ACH transactions and wire transfers.
- Transit Numbers: Used in Canada for domestic transactions and electronic fund transfers.
- Swift Codes: Used for international wire transfers and cross-border transactions.
Each type of bank transit number serves a specific purpose and is designed to meet the needs of different types of transactions. Understanding the differences between these numbers can help you choose the right one for your financial needs.
When to Use Each Type
The type of bank transit number you need depends on the nature of your transaction. For example, if you're setting up a direct deposit in the U.S., you'll need a routing transit number. If you're transferring funds internationally, you'll need a Swift code. Knowing which number to use can save you time and prevent errors.
How to Find Your Bank Transit Number
Locating your bank transit number is a straightforward process. Here are a few methods you can use:
- Check Your Bank Statement: Most bank statements include the transit number in the account details section.
- Online Banking Portal: Log in to your bank's website or mobile app and navigate to the account settings or profile section.
- Bank Website: Many banks provide transit number information on their official websites for customer convenience.
- Bank Check: The transit number is usually printed at the bottom of your checks, along with your account number and check number.
If you're unable to find your bank transit number using these methods, you can contact your bank's customer service department for assistance.
Tips for Verifying Your Bank Transit Number
To ensure accuracy, double-check your bank transit number before initiating any transactions. Mistakes in the number can result in failed or delayed transfers. If you're unsure about the validity of your transit number, consult your bank for confirmation.
Common Uses of Bank Transit Numbers
Bank transit numbers are used in a variety of financial transactions, including:
- Direct Deposits: Automating salary payments and government benefits.
- Electronic Fund Transfers (EFTs): Moving funds between accounts electronically.
- Bill Payments: Paying utility bills, loans, and other recurring expenses.
- Wire Transfers: Sending or receiving large sums of money domestically or internationally.
These applications make bank transit numbers an indispensable tool for managing personal and business finances. By understanding how to use them effectively, you can streamline your financial operations and reduce the risk of errors.
Differences Between Bank Transit Numbers and Routing Numbers
While the terms "bank transit number" and "routing number" are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between them. In the U.S., the term "routing number" is more commonly used, while in Canada, "transit number" is the preferred terminology. The primary distinction lies in their format and usage:
- Routing Numbers: Nine-digit codes used in the U.S. for domestic and international transactions.
- Transit Numbers: Eight-digit codes used in Canada for domestic transactions.
Both numbers serve the same purpose of identifying financial institutions, but their formats and applications differ based on regional banking systems.
When to Use Each Term
When communicating with banks or financial institutions, it's important to use the correct terminology. For example, if you're in the U.S., refer to the number as a "routing number." If you're in Canada, use the term "transit number" to avoid confusion.
Security Concerns with Bank Transit Numbers
While bank transit numbers are essential for financial transactions, they can also pose security risks if mishandled. Sharing your transit number with unauthorized parties can lead to fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized transfers or identity theft. To protect yourself, follow these security tips:
- Never share your transit number unless absolutely necessary.
- Use secure communication channels when transmitting sensitive information.
- Monitor your bank statements regularly for suspicious activity.
- Enable multi-factor authentication on your online banking accounts.
By taking these precautions, you can safeguard your financial information and reduce the risk of fraud.
The History of Bank Transit Numbers
The concept of bank transit numbers dates back to the early 20th century when the banking industry sought to standardize transaction processing. The introduction of routing transit numbers in the U.S. in 1911 marked a significant milestone in the evolution of banking systems. Over time, these numbers have become an integral part of modern financial infrastructure, enabling efficient and secure transactions on a global scale.
Today, bank transit numbers continue to evolve with advancements in technology and the increasing demand for digital banking services. Their role in facilitating electronic transactions remains as critical as ever.
Tips for Managing Bank Transit Numbers
To make the most of your bank transit number, consider the following tips:
- Keep your transit number in a secure location.
- Verify the number before initiating any transactions.
- Use online banking tools to manage your accounts efficiently.
- Stay informed about changes in banking regulations and practices.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your financial transactions are processed accurately and securely.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a bank transit number is a vital component of the banking system, enabling seamless and secure transactions. Whether you're setting up direct deposits, paying bills, or transferring funds, understanding how bank transit numbers work is essential for managing your finances effectively.
We encourage you to take action by verifying your bank transit number and using it wisely in your financial activities. Share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and explore our other resources for more insights into personal finance and banking. Together, we can build a more informed and financially secure future.