Understanding the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is crucial for anyone interested in plant biology, energy production, or environmental science. These reactions are the first stage of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy. This article will delve into what the light-dependent reactions produce, their mechanisms, and their importance in sustaining life on Earth.
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process that sustains life on Earth by converting sunlight into chemical energy. The light-dependent reactions play a pivotal role in this process, serving as the engine that powers the production of energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH. These molecules are essential for the subsequent stages of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
In this article, we will explore the intricate details of the light-dependent reactions, including the products they generate, the steps involved, and their significance in the broader context of photosynthesis. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of why these reactions are vital for both plants and the planet as a whole.
Read also:Michael Douglas Age A Comprehensive Look At His Life Career And Legacy
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Light-Dependent Reactions
- What Do Light-Dependent Reactions Produce?
- The Process of Light-Dependent Reactions
- The Role of ATP and NADPH
- Where Do Light-Dependent Reactions Occur?
- Photosystems and Electron Transport Chain
- Variations in Light-Dependent Reactions
- Why Are Light-Dependent Reactions Important?
- Light-Dependent vs. Light-Independent Reactions
- Future Research in Light-Dependent Reactions
Introduction to Light-Dependent Reactions
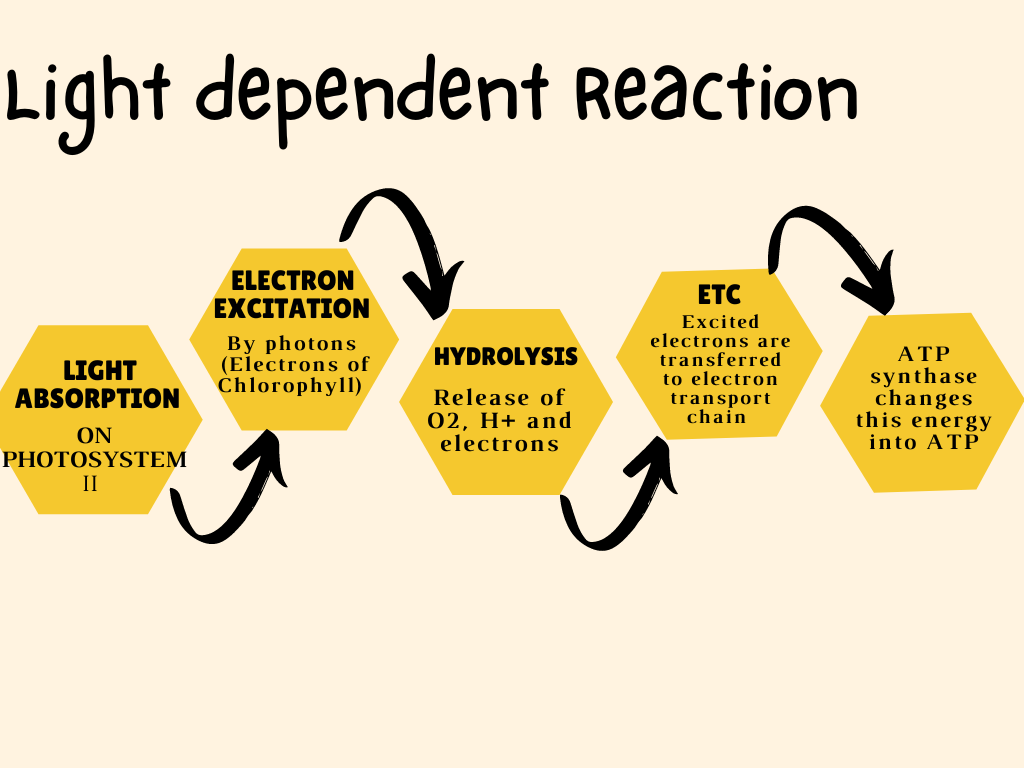
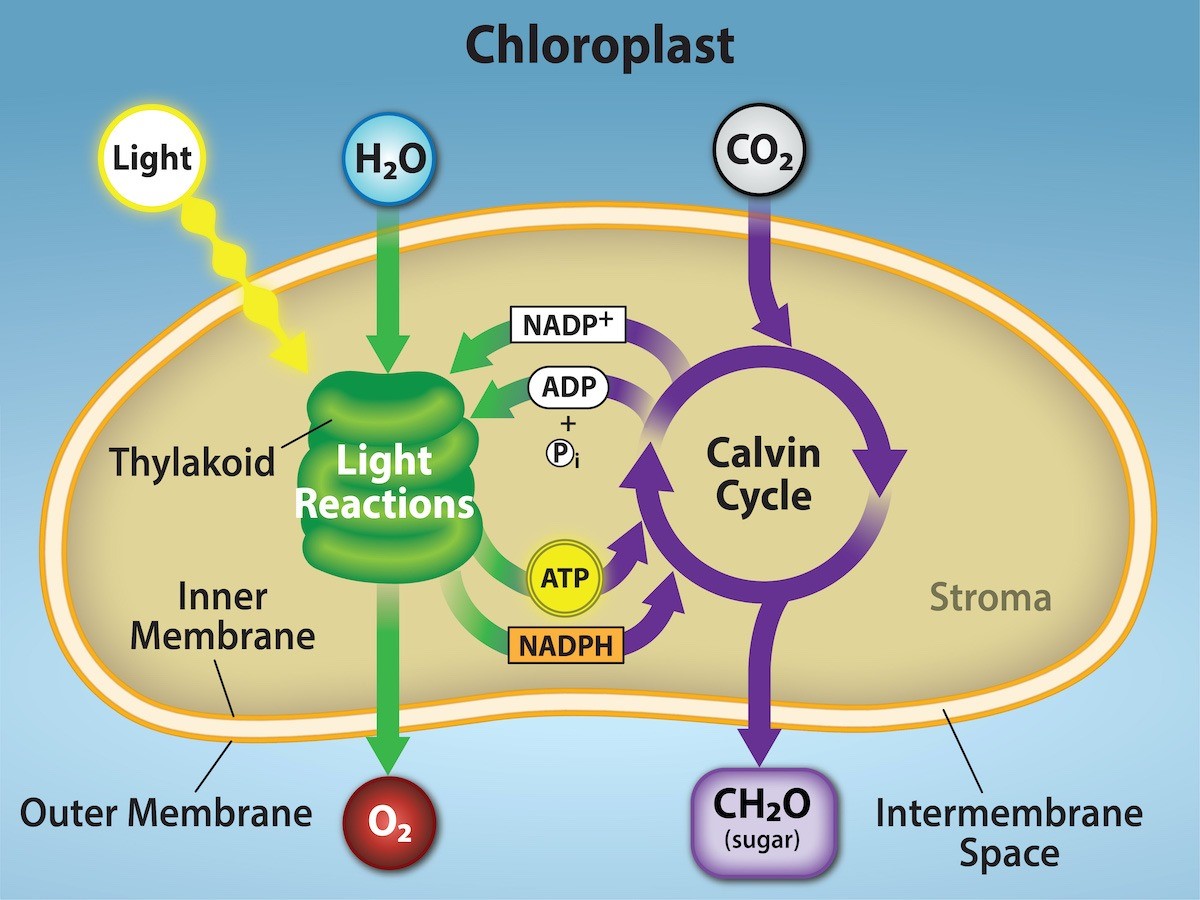
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are the initial steps in the conversion of solar energy into chemical energy. These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light by pigments such as chlorophyll. The energy from sunlight is used to split water molecules (photolysis), producing oxygen as a byproduct and generating high-energy molecules like ATP and NADPH.
This stage of photosynthesis is dependent on light, hence the name "light-dependent reactions." Without these reactions, plants would not be able to produce the energy required for growth, reproduction, and survival. Understanding the mechanisms behind these reactions is essential for fields such as agriculture, environmental science, and renewable energy research.
What Do Light-Dependent Reactions Produce?
The primary products of the light-dependent reactions are ATP, NADPH, and oxygen. These molecules are crucial for the continuation of photosynthesis and other cellular processes. Below is a breakdown of each product:
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): ATP is the energy currency of cells. It stores energy in its phosphate bonds, which can be released during hydrolysis to power various cellular activities.
- NADPH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate): NADPH serves as a reducing agent in the Calvin cycle, providing electrons for the synthesis of glucose.
- Oxygen (O₂): Oxygen is released as a byproduct of water splitting. This gas is essential for aerobic organisms, including humans, who rely on it for respiration.
The Process of Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions involve several key steps:
1. Absorption of Light
Chlorophyll and other pigments absorb photons of light, exciting electrons to a higher energy state. This process occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
2. Electron Transport Chain
The excited electrons are transferred through a series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane, known as the electron transport chain. This movement drives the synthesis of ATP via chemiosmosis.
Read also:What Star Sign Is 7th July Discover Your Zodiac And Unveil Its Mysteries
3. Photolysis of Water
Water molecules are split into oxygen, protons (H⁺), and electrons. This process replenishes the electrons lost by chlorophyll and provides protons for the generation of ATP.
The Role of ATP and NADPH
ATP and NADPH are critical for the continuation of photosynthesis. ATP provides the energy needed for the Calvin cycle, while NADPH supplies the reducing power. Together, these molecules enable the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide, a process essential for plant growth and energy storage.
Where Do Light-Dependent Reactions Occur?
The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. These membranes contain the necessary pigments, proteins, and enzymes for the process. The stacked arrangement of thylakoids, known as grana, maximizes the surface area for light absorption and reaction efficiency.
Photosystems and Electron Transport Chain
Two main photosystems are involved in the light-dependent reactions:
1. Photosystem II (PSII)
PSII absorbs light and initiates the splitting of water molecules. It is responsible for generating oxygen as a byproduct.
2. Photosystem I (PSI)
PSI captures additional light energy to boost the electrons to an even higher energy state, enabling the production of NADPH.
The electron transport chain connects these two photosystems, ensuring a continuous flow of electrons and efficient energy conversion.
Variations in Light-Dependent Reactions
Different organisms may exhibit variations in the light-dependent reactions. For example, cyanobacteria and algae perform similar processes but with slight differences in pigments and mechanisms. These variations allow for adaptation to different environments and light conditions.
Why Are Light-Dependent Reactions Important?
The light-dependent reactions are vital for several reasons:
- Oxygen Production: The release of oxygen supports aerobic life on Earth.
- Energy Storage: ATP and NADPH provide the energy and reducing power needed for the Calvin cycle.
- Climate Regulation: Photosynthesis helps regulate atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, mitigating the effects of climate change.
Light-Dependent vs. Light-Independent Reactions
While light-dependent reactions occur in the presence of light, light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) can take place in the absence of light. The former produces ATP and NADPH, while the latter uses these molecules to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide.
Future Research in Light-Dependent Reactions
Advancements in biotechnology and molecular biology are expanding our understanding of light-dependent reactions. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance photosynthetic efficiency, develop artificial photosynthesis systems, and address global challenges such as food security and renewable energy production.
Conclusion
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis produce ATP, NADPH, and oxygen, which are essential for life on Earth. These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involve the absorption of light, electron transport, and water splitting. Understanding their mechanisms and importance is crucial for various scientific fields and addressing global challenges.
We encourage you to share this article and explore related topics on our website. Your feedback and questions are always welcome in the comments section below. Together, we can deepen our knowledge of the natural world and its incredible processes.
Data Source: NCBI, Nature, ScienceDirect.