When we think of mountains, our minds often drift to towering peaks like Mount Everest. However, beneath the vast oceans lies a colossal geological wonder that rivals the giants above the surface. The largest mountain in the world underwater, Mauna Kea, is a marvel that demands attention. This article dives deep into the mysteries of this underwater giant, exploring its formation, significance, and impact on our understanding of Earth's geology.
Beneath the waves, there exists a realm of breathtaking natural wonders. Among these marvels, the largest mountain in the world underwater stands as a testament to the planet's incredible geological processes. This hidden titan, Mauna Kea, stretches from the ocean floor to the surface, surpassing even the mighty Mount Everest in sheer height.
In this article, we will unravel the secrets of Mauna Kea, from its formation to its role in shaping our understanding of underwater geography. Join us as we embark on a journey to explore the depths of the ocean and uncover the mysteries of this extraordinary underwater mountain.
Read also:World War 2 Events In Chronological Order A Comprehensive Timeline
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Mauna Kea
- Formation and Geological Processes
- Comparison with Other Mountains
- Impact on Marine Ecosystems
- Exploration and Scientific Research
- Challenges in Studying Underwater Mountains
- Significance in Geology
- Underwater Tourism and Conservation
- Future Discoveries and Exploration
Introduction
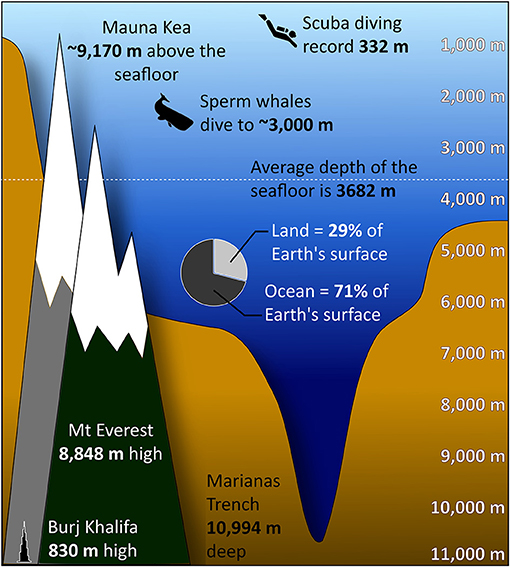
While Mount Everest holds the title of the highest peak above sea level, the largest mountain in the world underwater, Mauna Kea, is a geological marvel that stretches an impressive 10,203 meters (33,474 feet) from its base on the ocean floor to its summit above sea level. This makes it taller than Mount Everest when measured from base to peak.
Overview of Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea is an inactive volcano located on the Big Island of Hawaii. It is part of the Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain, a series of volcanic mountains that stretch across the Pacific Ocean. The mountain's underwater portion accounts for the majority of its height, making it a significant feature of the ocean floor.
Key Features of Mauna Kea
- Height from base to summit: 10,203 meters
- Summit elevation above sea level: 4,207 meters
- Location: Pacific Ocean, near Hawaii
- Geological classification: Shield volcano
Formation and Geological Processes
The formation of Mauna Kea is a result of tectonic activity and volcanic processes. Over millions of years, the Pacific Plate moved over a hotspot in the Earth's mantle, leading to the creation of the Hawaiian Islands. This hotspot fueled the volcanic activity that built Mauna Kea from the ocean floor to its current height.
Volcanic Activity and Tectonic Movement
Mauna Kea's formation began approximately 1 million years ago. The continuous eruption of magma from the hotspot created layers of basaltic rock, gradually building the mountain. As the Pacific Plate shifted, the hotspot moved, leaving Mauna Kea behind as a dormant volcano.
Comparison with Other Mountains
While Mount Everest is the tallest mountain above sea level, Mauna Kea surpasses it in overall height when measured from its base. This comparison highlights the importance of considering underwater geography when assessing geological features.
Height Comparison
- Mauna Kea: 10,203 meters (base to summit)
- Mount Everest: 8,848 meters (above sea level)
Impact on Marine Ecosystems
The presence of Mauna Kea has a profound impact on the marine ecosystems surrounding it. The underwater mountain creates unique habitats for a variety of marine species, including coral reefs, fish, and other organisms. The nutrient-rich waters around Mauna Kea support a diverse range of life forms.
Read also:Are Kimbra And Gotye Married Unveiling The Truth Behind Their Relationship
Biodiversity Around Mauna Kea
Studies have shown that the waters around Mauna Kea are home to numerous endemic species. The mountain's structure provides shelter and breeding grounds for various marine creatures, contributing to the biodiversity of the region.
Exploration and Scientific Research
Exploring the largest mountain in the world underwater presents unique challenges and opportunities for scientific research. Advances in technology have allowed scientists to study Mauna Kea in greater detail, revealing insights into its formation and impact on the surrounding environment.
Technological Advances in Exploration
- Submersibles and ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles)
- Advanced sonar mapping techniques
- Deep-sea drilling projects
Challenges in Studying Underwater Mountains
Studying underwater mountains like Mauna Kea poses several challenges, including harsh environmental conditions, limited access, and high costs. Researchers must overcome these obstacles to gain a comprehensive understanding of these geological wonders.
Key Challenges
- Extreme pressure at great depths
- Low visibility and darkness
- Logistical and financial constraints
Significance in Geology
The largest mountain in the world underwater plays a crucial role in our understanding of Earth's geology. By studying Mauna Kea, scientists can gain insights into plate tectonics, volcanic processes, and the evolution of oceanic features.
Geological Insights
Mauna Kea serves as a natural laboratory for geologists, providing valuable data on the formation and evolution of volcanic mountains. Its study contributes to our knowledge of Earth's dynamic processes and helps predict future geological events.
Underwater Tourism and Conservation
The unique beauty of Mauna Kea has made it a popular destination for underwater tourism. Divers and researchers alike are drawn to its stunning landscapes and rich biodiversity. However, conservation efforts are essential to protect this fragile ecosystem from human impact.
Conservation Initiatives
Efforts to preserve the marine life around Mauna Kea include the establishment of marine protected areas, sustainable tourism practices, and public awareness campaigns. These initiatives aim to ensure the long-term health and survival of the region's ecosystems.
Future Discoveries and Exploration
As technology continues to advance, the exploration of underwater mountains like Mauna Kea will undoubtedly lead to new discoveries and a deeper understanding of our planet. Future research may uncover hidden geological features and reveal the secrets of Earth's hidden depths.
Potential Future Discoveries
- Unexplored underwater ecosystems
- Previously unknown geological formations
- Insights into Earth's climate history
Conclusion
The largest mountain in the world underwater, Mauna Kea, is a testament to the incredible geological processes that shape our planet. From its formation to its impact on marine ecosystems, this hidden titan offers a wealth of knowledge and inspiration for scientists and explorers alike. As we continue to explore the depths of the ocean, we uncover new mysteries and gain a greater appreciation for the wonders of our world.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments below. Do you have any questions about Mauna Kea or underwater geography? Feel free to ask, and don't forget to explore other fascinating articles on our site. Together, let's dive deeper into the mysteries of our planet!
Data Sources:

/https://tf-cmsv2-photocontest-smithsonianmag-prod-approved.s3.amazonaws.com/58ab2015-dd1e-48ac-94b4-4222cc12ea31.jpg)