Bank transit numbers play a crucial role in financial transactions, yet many people are unfamiliar with their purpose and importance. If you’ve ever wondered, "What is a transit number?" or how it impacts banking processes, this article will provide you with a detailed explanation. Whether you're transferring funds or setting up direct deposits, understanding transit numbers is essential for ensuring smooth financial operations.
A transit number, also known as a routing transit number (RTN) or bank transit number, is a unique code assigned to financial institutions to identify them during transactions. This number ensures that money reaches the correct bank branch and account. It is particularly important in countries like Canada and the United States, where banking systems rely heavily on these codes for processing payments.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of what transit numbers are, how they function, and why they are critical in modern banking systems. Let's dive in and explore the world of transit numbers in detail.
Read also:Dakota Culkin Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Transit Numbers
- What Exactly is a Transit Number?
- Transit Numbers in Canada
- Routing Transit Numbers in the USA
- Structure and Format of Transit Numbers
- The Purpose of Transit Numbers
- How Transit Numbers Are Used
- Differences Between Transit Numbers and SWIFT Codes
- How to Find Your Transit Number
- Security Concerns and Best Practices
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Introduction to Transit Numbers
Before we delve into the specifics, it's important to recognize the foundational role transit numbers play in banking systems. These numbers are not just random codes; they are carefully assigned identifiers that streamline financial processes. For instance, when you initiate an electronic funds transfer, the transit number ensures that the transaction is routed to the correct bank and branch.
In today's digital age, where online banking and electronic payments dominate, understanding transit numbers becomes even more critical. They serve as a backbone for secure and efficient financial transactions, ensuring that money reaches its intended destination without errors.
What Exactly is a Transit Number?
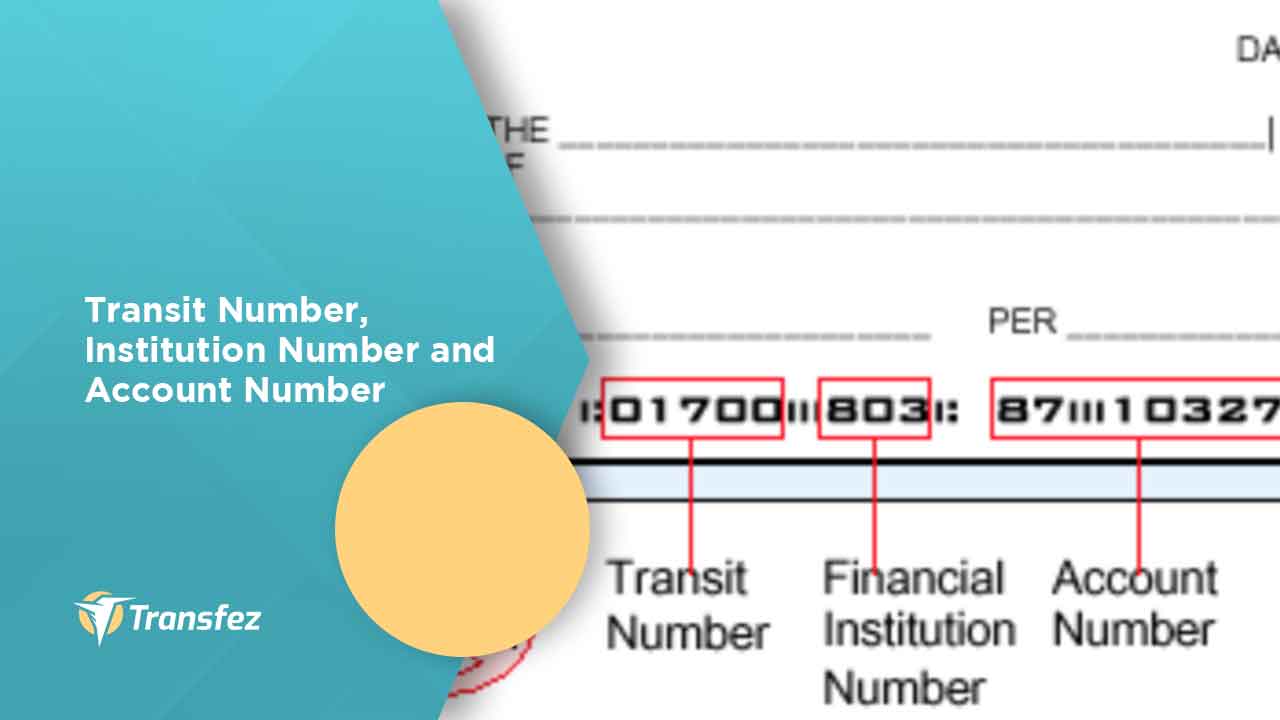
A transit number is a unique code used to identify a specific bank or financial institution. In Canada, it typically consists of five digits followed by a hyphen and three digits, representing the branch number and the institution number, respectively. In the United States, the routing transit number (RTN) is a nine-digit code that performs a similar function.
Key Components of Transit Numbers
- Branch Number: Identifies the specific branch of the bank.
- Institution Number: Identifies the financial institution itself.
- Hyphen: Acts as a separator between the branch and institution numbers.
These components work together to ensure accurate identification of banks and branches during transactions.
Transit Numbers in Canada
In Canada, transit numbers are commonly used for domestic transactions such as direct deposits, bill payments, and wire transfers. The format is standardized, making it easy for both banks and customers to use them effectively.
Structure of Canadian Transit Numbers
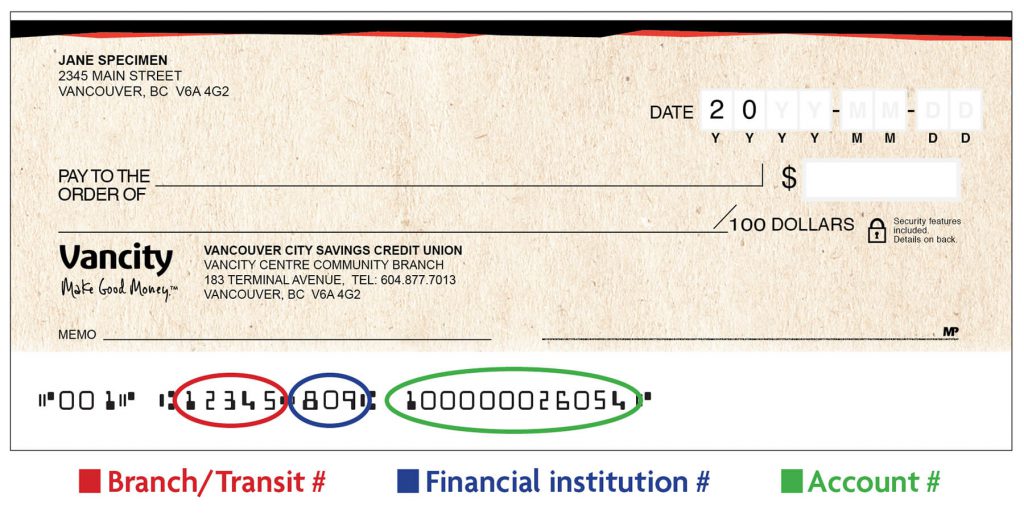
Canadian transit numbers follow a specific format: **AAAAA-BBB**, where:
Read also:George Jung And Daughter A Journey Through The Infamous Life Of A Drug Kingpin And His Family
- AAAAA: Represents the branch number.
- B: Represents the institution number.
This standardized format ensures consistency and accuracy in financial transactions across the country.
Routing Transit Numbers in the USA
In the United States, routing transit numbers (RTNs) serve the same purpose as transit numbers in Canada but have a slightly different format. RTNs consist of nine digits and are used for electronic transactions such as Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments and wire transfers.
Importance of RTNs in the USA
RTNs are critical for processing payments in the United States. They ensure that funds are routed to the correct bank and account, minimizing errors and delays. According to the American Bankers Association (ABA), RTNs are an integral part of the U.S. banking system, facilitating millions of transactions daily.
Structure and Format of Transit Numbers
Understanding the structure of transit numbers is essential for using them correctly. Whether you're dealing with Canadian transit numbers or U.S. RTNs, knowing the format helps prevent mistakes during financial transactions.
Canadian Transit Number Format
As mentioned earlier, Canadian transit numbers follow the **AAAAA-BBB** format. This format ensures that each bank branch has a unique identifier, reducing the risk of errors during transactions.
U.S. Routing Transit Number Format
U.S. RTNs consist of nine digits, with the first four digits representing the Federal Reserve Routing Symbol, the next four digits identifying the bank, and the final digit serving as a checksum.
The Purpose of Transit Numbers
The primary purpose of transit numbers is to facilitate accurate and efficient financial transactions. They ensure that funds are routed to the correct bank and account, minimizing errors and delays. Whether you're setting up a direct deposit, paying bills online, or transferring money electronically, transit numbers play a vital role in ensuring that the transaction is processed correctly.
Key Functions of Transit Numbers
- Identifying specific banks and branches.
- Facilitating electronic fund transfers.
- Ensuring accurate routing of payments.
Without transit numbers, the banking system would be prone to errors and inefficiencies, making it difficult to process transactions accurately.
How Transit Numbers Are Used
Transit numbers are used in various financial transactions, including direct deposits, bill payments, and wire transfers. They ensure that funds are routed to the correct bank and account, minimizing errors and delays.
Examples of Transit Number Usage
- Direct Deposits: Employers use transit numbers to deposit salaries directly into employees' bank accounts.
- Bill Payments: Customers use transit numbers to pay bills online or through automated systems.
- Wire Transfers: Transit numbers are essential for transferring large sums of money between banks.
By understanding how transit numbers are used, you can ensure that your financial transactions are processed smoothly and efficiently.
Differences Between Transit Numbers and SWIFT Codes
While transit numbers and SWIFT codes both serve to identify financial institutions, they differ in scope and usage. Transit numbers are primarily used for domestic transactions, while SWIFT codes are used for international transactions.
Key Differences
- Scope: Transit numbers are used for domestic transactions, while SWIFT codes are used for international transactions.
- Format: Transit numbers follow a standardized format specific to each country, while SWIFT codes consist of 8-11 alphanumeric characters.
- Purpose: Transit numbers ensure accurate routing of domestic payments, while SWIFT codes facilitate secure international transfers.
Understanding the difference between these two codes is essential for navigating the global banking system effectively.
How to Find Your Transit Number
Finding your transit number is a straightforward process. You can locate it on your bank statements, checks, or by contacting your bank directly. Most banks also provide this information on their websites or mobile apps.
Steps to Find Your Transit Number
- Check your bank statements or checks for the transit number.
- Visit your bank's website or mobile app for online access to your transit number.
- Contact your bank's customer service for assistance if needed.
By following these steps, you can easily obtain your transit number and ensure that your financial transactions are processed accurately.
Security Concerns and Best Practices
While transit numbers are essential for financial transactions, they also pose potential security risks if not handled properly. It's important to protect your transit number and other sensitive financial information to prevent unauthorized access and fraud.
Best Practices for Security
- Never share your transit number or account information with unauthorized individuals.
- Use secure methods for transmitting financial information, such as encrypted email or secure online portals.
- Monitor your bank statements regularly for any suspicious activity.
By following these best practices, you can safeguard your financial information and ensure the security of your transactions.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, transit numbers are essential components of the banking system, ensuring accurate and efficient financial transactions. Whether you're dealing with Canadian transit numbers or U.S. RTNs, understanding their purpose and usage is crucial for navigating the modern banking landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- Transit numbers identify specific banks and branches during financial transactions.
- They are used for domestic transactions such as direct deposits, bill payments, and wire transfers.
- While transit numbers and SWIFT codes serve similar purposes, they differ in scope and usage.
- Protecting your transit number and other sensitive financial information is essential for ensuring the security of your transactions.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from understanding transit numbers. For more informative content on banking and finance, explore our other articles on the website. Your feedback and questions are always welcome in the comments section below!