Class, phylum, and order are essential components of the biological classification system used to categorize living organisms systematically. These ranks form the backbone of taxonomy, enabling scientists to understand the relationships between different species. By studying these classifications, we gain insights into the evolutionary history and biodiversity of life on Earth.
Understanding taxonomy is crucial for both students and researchers alike. It provides a framework to organize and analyze the vast diversity of life forms. The hierarchical structure of taxonomy helps scientists communicate more effectively about organisms and their relationships to one another.
In this article, we will explore the significance of class, phylum, and order in biological classification. We will delve into their definitions, examples, and the role they play in the broader context of taxonomy. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these taxonomic ranks and their importance in the scientific community.
Read also:Shellac Beetle Understanding The Intriguing World Of This Unique Insect
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Taxonomy
- Definition of Class
- Definition of Phylum
- Definition of Order
- Examples of Classification
- The Taxonomic Hierarchy
- Importance of Taxonomy
- Methods of Classification
- Evolutionary Significance of Taxonomy
- The Future of Taxonomy
- Conclusion
Introduction to Taxonomy
Taxonomy is the scientific discipline of naming, defining, and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. The system of classification helps scientists understand the relationships between different species and their evolutionary history. At the heart of this system are the ranks of class, phylum, and order, which provide a structured way to categorize life forms.
Carl Linnaeus, often referred to as the "father of modern taxonomy," developed the binomial nomenclature system in the 18th century. This system laid the foundation for the hierarchical classification of organisms. Today, taxonomy continues to evolve, incorporating new discoveries and advancements in molecular biology and genetics.
Definition of Class
In taxonomy, a class is a rank that sits above order and below phylum. It is used to group organisms with similar characteristics into broader categories. For example, mammals, reptiles, and birds are all classes within the phylum Chordata.
Characteristics of Class
- Classes group organisms with shared physical and genetic traits.
- They provide a middle ground between broader and narrower taxonomic ranks.
- Classes help scientists understand the evolutionary relationships between organisms.
According to a study published in the National Library of Medicine, the classification of organisms into classes is crucial for understanding biodiversity and ecological interactions.
Definition of Phylum
A phylum is a taxonomic rank that sits above class and below kingdom. It is one of the most significant ranks in the classification system, as it represents a major division of life forms. For example, the phylum Chordata includes all animals with a notochord, such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Key Features of Phylum
- Phyla are defined by fundamental body plans and structural characteristics.
- They represent a higher level of classification, encompassing a wide range of species.
- Phyla help scientists identify evolutionary trends and patterns across different groups of organisms.
Research conducted by the National Geographic Society highlights the importance of phyla in understanding the diversity of life on Earth.
Read also:Twisty Amanozako Past Life Unveiling The Mysteries And Secrets
Definition of Order
An order is a taxonomic rank that sits above family and below class. It is used to group organisms with similar characteristics into more specific categories. For example, the order Carnivora includes mammals such as lions, bears, and wolves, which share common traits related to their diet and anatomy.
Significance of Order
- Orders provide a detailed classification of organisms based on specific traits.
- They help scientists study the relationships between closely related species.
- Orders are essential for understanding the ecological roles of different organisms.
The Encyclopedia Britannica provides comprehensive information on the classification of organisms into orders, emphasizing their importance in biological research.
Examples of Classification
To better understand the concept of class, phylum, and order, let us examine some examples of how these ranks are applied in taxonomy:
Example 1: Human Classification
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
Example 2: Oak Tree Classification
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Phylum: Tracheophyta
- Class: Magnoliopsida
- Order: Fagales
These examples demonstrate how class, phylum, and order are used to systematically classify organisms based on their characteristics.
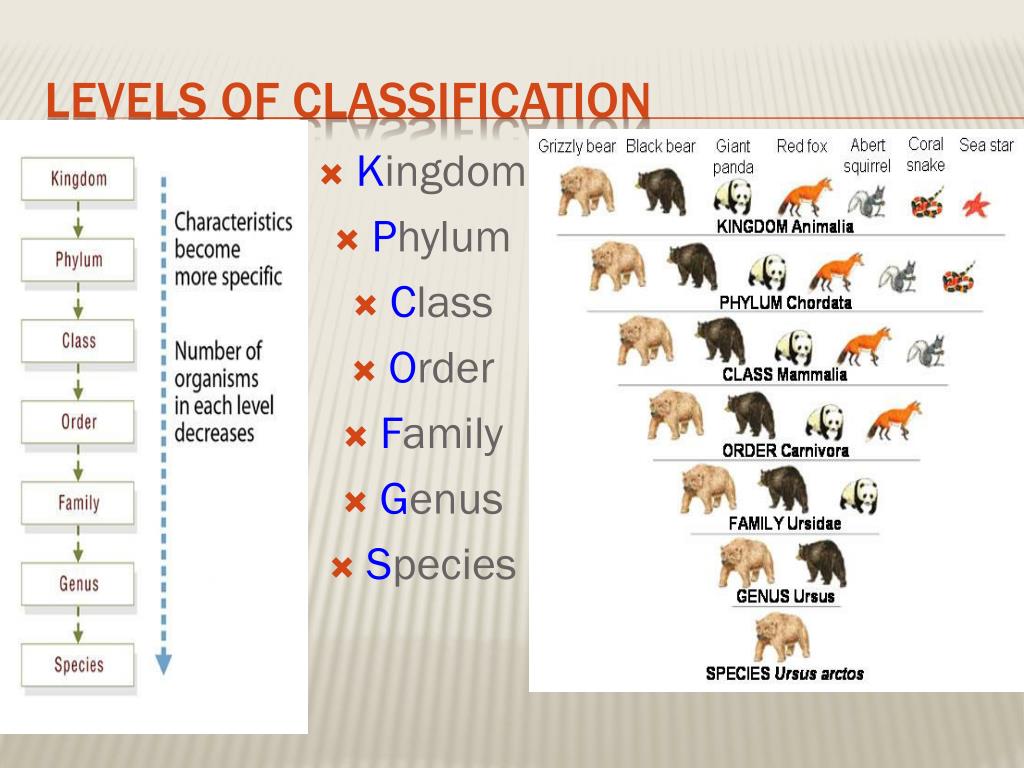
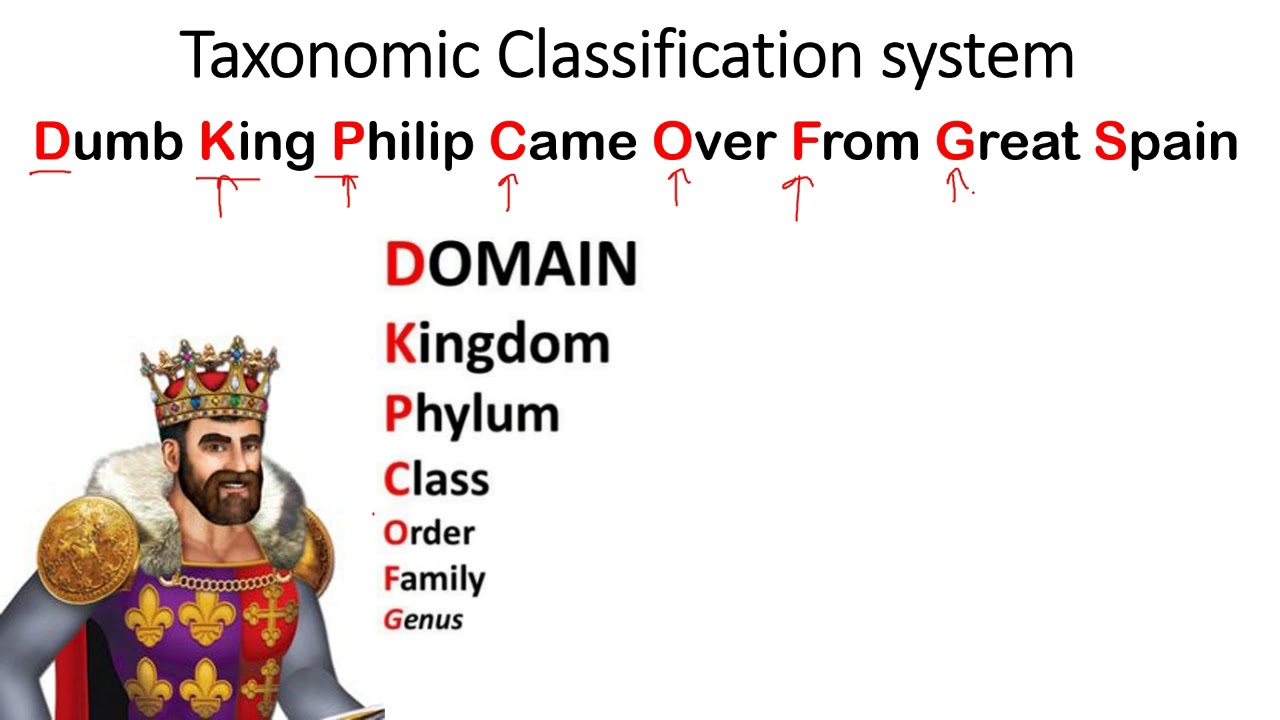
The Taxonomic Hierarchy
The taxonomic hierarchy is a system of classification that organizes living organisms into a series of ranks, from the broadest to the most specific. The hierarchy includes the following ranks:
- Domain
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
Each rank provides a level of detail that helps scientists understand the relationships between organisms. Class, phylum, and order are crucial components of this hierarchy, bridging the gap between broader and narrower classifications.
Importance of Taxonomy
Taxonomy plays a vital role in the scientific community by providing a standardized system for classifying organisms. This system facilitates communication, research, and conservation efforts. By understanding the relationships between different species, scientists can better predict ecological interactions and develop strategies for preserving biodiversity.
Applications of Taxonomy
- Ecological research: Taxonomy helps scientists study the interactions between organisms and their environments.
- Conservation biology: Accurate classification is essential for identifying endangered species and developing conservation plans.
- Medical research: Taxonomy aids in the identification of pathogens and the development of treatments for diseases.
According to the World Wildlife Fund, taxonomy is critical for protecting endangered species and maintaining ecological balance.
Methods of Classification
There are several methods used in taxonomy to classify organisms, including traditional morphology-based approaches and modern molecular techniques. These methods complement each other, providing a more comprehensive understanding of biodiversity.
Traditional Morphology-Based Classification
This method relies on the physical characteristics of organisms, such as size, shape, and structure, to classify them into different taxonomic ranks. While this approach has been used for centuries, it can be limited by convergent evolution, where unrelated organisms develop similar traits.
Molecular Classification
Molecular techniques, such as DNA sequencing, provide a more accurate way to classify organisms based on their genetic makeup. These methods have revolutionized taxonomy by revealing relationships between organisms that were previously unknown.
Evolutionary Significance of Taxonomy
Taxonomy is closely linked to the study of evolution, as it provides a framework for understanding the relationships between different species. By analyzing the characteristics of organisms at different taxonomic ranks, scientists can trace the evolutionary history of life on Earth.
Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees are diagrams that represent the evolutionary relationships between organisms. They are constructed using data from taxonomy, genetics, and paleontology, providing a visual representation of the tree of life.
Research published in the Nature journal highlights the importance of phylogenetic trees in understanding the evolutionary history of organisms.
The Future of Taxonomy
As technology continues to advance, the field of taxonomy is evolving to incorporate new tools and techniques. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics is transforming the way scientists classify and study organisms.
Emerging Trends in Taxonomy
- Genomic taxonomy: The use of DNA sequencing to classify organisms at a molecular level.
- Bioinformatics: The application of computational tools to analyze large datasets in taxonomy.
- Citizen science: Engaging the public in taxonomic research through crowdsourcing initiatives.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature emphasizes the importance of embracing new technologies in taxonomy to address global conservation challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, class, phylum, and order are essential components of the taxonomic system, providing a structured way to classify and understand the diversity of life on Earth. By studying these ranks, scientists can gain insights into the evolutionary history and relationships between different organisms. The importance of taxonomy extends beyond scientific research, playing a crucial role in conservation, medicine, and ecology.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website to deepen your understanding of biology and taxonomy. Together, we can continue to unravel the mysteries of life and preserve the incredible diversity of our planet.